1 Introduction and Overview of the Planning for Robotics in Construction
The construction industry is advancing towards automation in constructing buildings and infrastructure by deploying robotics into construction projects. Construction robotics can improve overall construction quality, improve jobsite safety, reduce the onsite workforce needs, and improve productivity. A challenge for construction project managers and superintendents is to identify and evaluate potential automation and robotics solutions on projects or within standard work activities within their company. Construction robotics appeared on sites in the 1980s, and since then, integrated automated building construction has been developed. However, implementing construction robotics on site makes it difficult to determine the starting point since the environment of a construction project changes over time, and various stakeholders need to be involved in the planning and execution. Adding to that, limited kinds of robotics are available in the market right now, which does not allow the construction team to choose whatever area they want to deploy. Since the technology is in the emerging era, some robotics costs might make it difficult for the team to get a return on the investment when focused on a single project, so in some cases, it is required to invest in a long-term investment.
This guide aims to provide champions and project teams with a systematic and well-formulated process for planning and executing the integration of construction robotics, enhancing the advancement of the construction industry towards automation. This process consists of 6 steps: Set Goals, Identify Opportunities, Evaluate Solutions, Make Decision, Communicate Plan, and Improve Implementation.
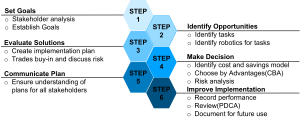
Figure 1.1. Planning Procedure for Robotics in Construction
Step1. Set Goals
One crucial step in this planning is to begin by clearly setting the construction team’s goal of implementing robotics on the field. These goals could be related to safety, faster schedule, higher quality, fulfilling the gap of an insufficient number of workers, or reducing cost. Once the team has established its goals, it can start finding solutions. By setting those goals, the team can have a strong backbone of the motivation to implement robotics. An approach for setting goals is presented in Chapter 2.
Step 2. Identify Opportunities
Once the team has identified the goals, the team can start identifying the current challenges to achieving them. Analyzing the challenges can reveal the construction tasks that are worth considering the use of robotics. Users of the guide can refer to a list of characteristics to see the ideal characteristics of the tasks to implement robotics. Uniformat is recommended for a systematic review of the list of construction tasks. After identifying the tasks, potential robotics related to those tasks can be identified. An approach for identifying robotics and opportunities is presented in Chapter 3.
Step 3. Evaluate Solutions
A procedure for evaluating identified robotics needs to be performed. One part of this is creating an implementation plan for each robotic to determine its feasibility. Another important part is discussing robotics with trades that could be impacted and having an open discussion to gather potential issues. Other factors to consider in creating an implementation plan are additional resources, schedule, site logistics, and onboarding. An approach for evaluating robotics is presented in Chapter 4.
Step 4. Make Decision
Once the implementation plan is developed, the team needs to focus on the cost. Once the cost information is clear, the team should conduct a risk registry. With all the necessary information to make a decision set on the table from previous steps, the team can decide whether to give the implementation a go or no go. This procedure is presented in Chapter 5.
Step 5. Communication Plan
After the team decided to implement robotics, the team should communicate about the decision including background discussion and detailed plan for implementation. It is recommended to use A3 planning for this communication. This procedure is further explained in Chapter 6.
Step 6. Improve Implementaion
The goal is not the implementation of robotics itself. It is critical to return to the goal set in Step 1 and look for continuous improvement. This step provides resources for users to monitor for a successful robotics implementation. This procedure is presented in Chapter 7.

