Chapter Four: Corrections

Chapter Four: CORRECTIONS
Why Do We Punish Criminals?
- Retribution
- Deterrence
- Incapacitation
- Rehabilitation
- Restorative Justice
Structure of Sentencing
- Indeterminate Sentencing
- A period of incarceration that is determined by the judge, operating within a set of minimum and maximum sentences determined by the legislature
- Determinate Sentencing
- A period of incarceration that is fixed by a sentencing authority and cannot be reduced by judges or other corrections officials.
- Good Time
- A reduction in time served by prisoners based on good behavior, conformity to rules, and other positive actions.
Truth- in- Sentencing – convicts will serve approximately the terms to which they were initially sentenced. 85%
Correction has 3 Levels
Reintegration - A goal of corrections that focuses on preparing the offender for a return to the community.
Diversion - A strategy to divert those offenders who qualify away from prison and jail and toward community- based and intermediate sanctions
Probation- A criminal sanction in which a convict is allowed to remain in the community rather than be imprisoned as long as she or he follows certain conditions set by the court
Intermediate Sanction
- Shock Incarceration
- Day Reporting Centers
- Drug Court
- Forfeiture
- Home Confinement
- Pretrial Diversion Programs
- Electronic Monitoring
- Intensive Supervision Probation
History of Penitentiary
- In 1776, PA passed legislation to switch from punishment to rehabilitation.
- PA opened first Penitentiary in 1790 -Walnut Street
- Penitentiary – An early form of correctional facility that emphasized separating inmates from society and from each other so that they would have an environment in which to reflect on their wrongdoing and ponder their reformation.
-
Opened in 1829 with the controversial goal of changing the behavior of the inmates instead of merely punishing them.
-
A essential part of this structure was the layout of the facility
-
Designed in the form of a wagon wheel. Known today as the radial style
-
The back to back cells in each spoke of the wheel faced outward from the center to limit contact among inmates.
-
Nearly 350 prisons around the US have been built to this same design.
Separate Confinement
-
A 19th century penitentiary system developed in Pa in which inmates were kept separate from each other at all times, with daily activities in the cell.
Congregate System
-
Developed in NY in which inmates were kept in separate cells during the night but would work together in the daytime under a code of enforced silence. Known as Auburn system
Medical Model
-
A model of corrections in which the psychological and biological roots of an intimate’s criminal behavior are identified and treated.
Increased Probability of Incarceration
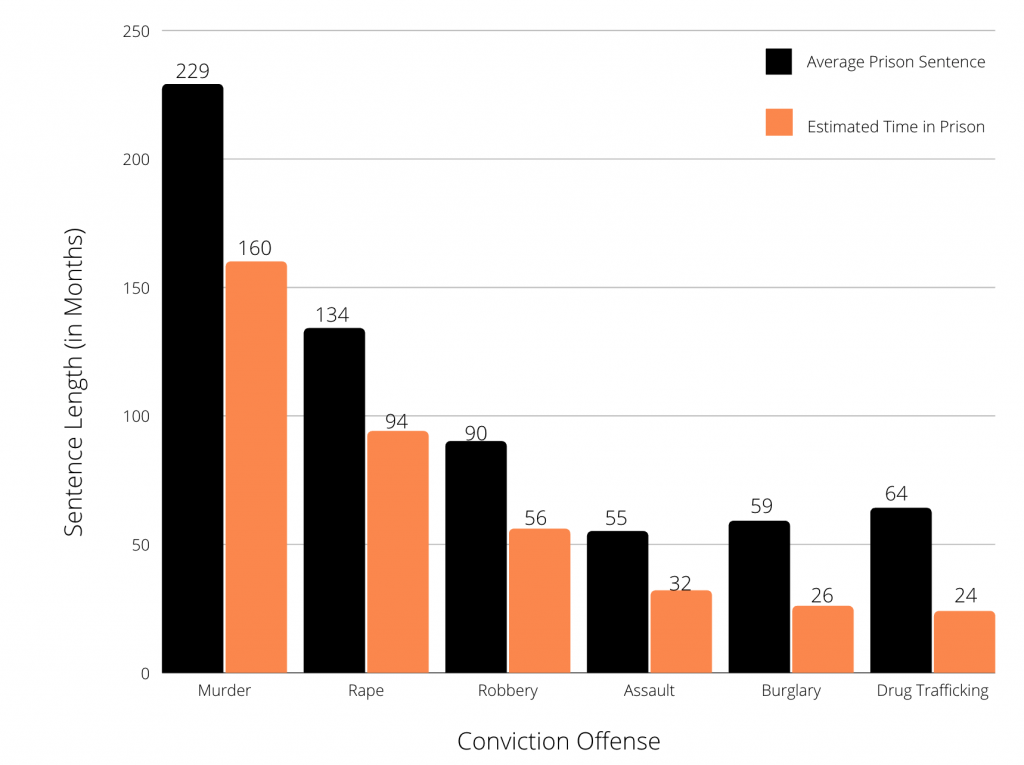
- The chance of someone who is arrested going to prison today is much greater than it was 20 years ago. Mostly this occurs in those arrested for murders, sexual assault and weapons offense.
Inmates Serving More Time for Each Crime
- After the Sentencing Reform Act in 1984, the length of time served by federal convicts for their crimes rose significantly.
- 6-10 convicted for drugs will serve a mandatory offense.
- States require truth in sentencing act which states that 85% of the sentence must be completed.
Federal Prison Growth
- The federal prison acquires 150,000 inmates which is the largest in the world. Also the gun possessions crimes that were passed by Clinton and Bush increases 68 % of the population in 1995-2001 along with immigration laws that increased by 133 % which represented 10% of the inmate population.
Rising Incarceration of Women
- 8% of inmates population
- Mandatory Minimums
Types of Prisons
- Maximum Security Prison
- A correctional institute designed and organized to control and discipline dangerous felons, as well as prevents escapes, with intense supervision cement walls, and electronic barbed wire fences.
- Medium Security Prison
- A correctional institute that houses less dangerous inmates and therefore uses less restrictive measures to avoid violence and escapes.
- Minimum Security Prisons
- A correctional institution designed to allow inmates most of whom pose low security risk a great deal of freedom of movement and contact with the outside world.
History of Correctional Institutions
- Original punishments were banishment, slavery, restitution, corporal punishment and execution.
- Jails have been run throughout history so that the sheriff can obtain financial gain.
- 1776 – Inmate population on the rise in Europe, Decided on use of Prison Hulks.
Corrections in US
- American correctional system originated in Pennsylvania under William Penn
- He revised the criminal codes to forbid any form of torture
- He emphasized hard labor, fines, and property forfeiture
PA System
- Single inmate to a cell
- Cell designed as a mini Prison
- Wagon Wheel Style
- Constant Solitary Confinement
Auburn System
- Was created due to the constant overcrowding in the PA system
- Based on the fear of punishment
- Silence for all
- Inmates worked all day and then in cells at night.
Developing Prison System
- Michael Foucault’s Theory of Development
- Punishments evolves with society
- Complex Societies seek complex forms of punishment
- Punishment evolved from physical to psychological
- Auburn system was the best suited for the US and the PA system was only used for worst inmates. (Segregation in the SHU)
Jails
- Relieve prison overcrowding
- Used as pretrial detention
- Used of inmates who need to be sentenced
- Confinement of Misdemeanors
- Probation and Parole Violations
Jail Demographics
- 15,000 Municipal, can only hold you for __ hours
- County Jails can hold inmates for up to ___ year
- Annual increase in population is around 4-5%
- 50,000 Youths are admitted to jail each year
- 90% of population are male
Jail Conditions
- Lowest Priority in the System
- Based on Taxes
- Overcrowded and ineffective
Gender
- Women underrepresented
- Male to female Arrest ratio = 3:5 overall, Violent crimes 1:5
- Most female inmates are in for less serious crimes
Minorities
- Prison is Predominately minority
- 16% of black males between the ages of 25-29 are in prison.
Types of Offenses
- A little of ½ of all inmates are serving time for violent behavior.
- Inmates who are in for doing time for drug related offenses is increasing year after year
Substance Abuse
- Strong association in prison between substance use and inmate status
- 50% under the influence at time of arrest.
Physical Abuse
- About 19% of all inmates have a history of prior physical abuse before entering prison
- Mental Health issues
- Only a few members of the middle and upper class end up in prison
Camps
Farms – located in the South and west, agricultural emphasize.
Ranches
- Raise Cattle
- Breed Horses
- 60 in operation mostly in the west
Road Camps
- Repair Roads and Highways
- 80 in US
Types of Prison Release
Separate System for Kids
-
- The Child Saving Movement
- Parents Patriae- A doctrine that holds that the state has a responsibility to look after the well- being of children.
- The first case of abuse
- The Child Saving Movement
Juvenile Delinquency
- Status Offender
- A juvenile who has been found to have engaged in behavior deemed unacceptable for those under a certain statutorily determined age. EX.
- Juvenile Delinquency
- Behavior that is illegal under federal or state law that has been committed by a person who is under an age limit specified by statute.
Constitutional Protections
- Kent v United States – Due Process for Juveniles
- In re Gault – right to counsel, and not self incrimination.
How Delinquency is Determined
Competency– The mental capacity of an individual to participate in legal proceedings, based on that person’s ability to understand the nature of the those proceedings.
Free Crime – Who are you in class with?
Bank Robbers – 11
Killer – 2
Car Jacking – 2
Smoke Dope – 1
Free Defenders – 1
Speeding -1
Burglary – 1
Rooftop Jumping -1
Punishment Terms
- Judicial Waiver
- Detention
- Graduated Sanctions
- Residential Treatment Facility (RTF)
- Training Schools
-
Juvenile Probation
-
Secure Confinement
-
Boot Camp
-
Aftercare
-
The variety of therapeutic, educational, and counseling programs for juvenile delinquents (and some adults) after they have been released from a correctional facility.
-
Terrorism
Terms
The Patriot Act makes it easier for law enforcement agents to conduct searches
– Patriot Act amends the law to allow the FBI or other federal agency to obtain warrants for “terrorism” investigations, “chemical weapons” investigations, or “computer fraud and abuse” investigations as long as agents can prove that such actions have a “significant purpose.” In other words, no proof of criminal activity need be provided.

