8 Monopoly
8.1 an introduction to monopoly
Review Activities
No review activities for this section.
Problems
No problems for this section.
External Resources
Khan Academy: Perfect and Imperfect Competition
Khan Academy: Monopolies vs. Perfect Competition
8.2 barriers to entry
Review Activities
Problems
No problems for this section.
External Resources
No videos for this section.
8.3 monopolies and profit-maximization
Review Activities
Problems
Problem 8.3.1: A monopolist faces the following demand curve. Complete the table below.
| Q | P | TR | AR | MR |
| 0 | 30 | XX | XX | |
| 1 | 25 | |||
| 2 | 20 | |||
| 3 | 15 | |||
| 4 | 10 | |||
| 5 | 5 |
Solutions: $0; $25, $25, $25; $40, $20, $15; $45, $15, $5; $40, $10, -$5; $25, $5, $-15
Problem 8.3.2: A monopolist faces the following demand curve. Complete the table below.
| Q | P | TR | AR | MR |
| 0 | 30 | XX | XX | |
| 1 | 26 | |||
| 2 | 20 | |||
| 3 | 17 | |||
| 4 | 12 |
Solutions: $0; $26, $26, $26; $40, $20, $14; $51, $17, $11; $48, $12, -$3
Problem 8.3.3: A monopolist faces the following demand and cost schedules. Complete the table below. Find the profit-maximizing level of production as well as the profit-maximizing price. Be sure to use the profit-maximization condition. What is the maximum possible profit?
| Q | P | TR | TC | Tπ | MR | MC |
| 0 | 50 | 20 | ||||
| 1 | 45 | 25 | ||||
| 2 | 40 | 33 | ||||
| 3 | 35 | 45 | ||||
| 4 | 30 | 60 | ||||
| 5 | 25 | 80 | ||||
| 6 | 20 | 110 | ||||
| 7 | 15 | 150 | ||||
| 8 | 10 | 200 |
Solutions: See video for table. P=$30, Q=4, π=$60
Problem 8.3.4: A monopolist faces the following demand and cost schedules.
| Q | P | TR | TC | Tπ | MR | MC |
| 7 | 90 | 210 | ||||
| 8 | 87 | 230 | ||||
| 9 | 84 | 260 | ||||
| 10 | 81 | 300 | ||||
| 11 | 78 | 348 | ||||
| 12 | 74 | 408 | ||||
| 13 | 70 | 475 |
- Complete the table below.
- Find the profit-maximizing level of production as well as the profit-maximizing price. Be sure to use the profit-maximization condition. What is the maximum possible profit?
- Re-consider problems 1 and 2. Instead of a monopolist, the firm is now in a perfectly competitive market where the market price is $60. What is this firm’s profit-maximizing price and level of output? How much profit will it earn? Calculate the difference between the monopolist’s profit and the competitive firm’s profit. You do not need to make a new table, but can if you want to.
Solutions: See video for table; Q=11, P=$78, π=$510; P=$60, Q=12, π=$312, Monopolist earns $198 more than in PC.
Problem 8.3.5: Use the graph below to determine the profit-maximizing price and output for the monopolist.
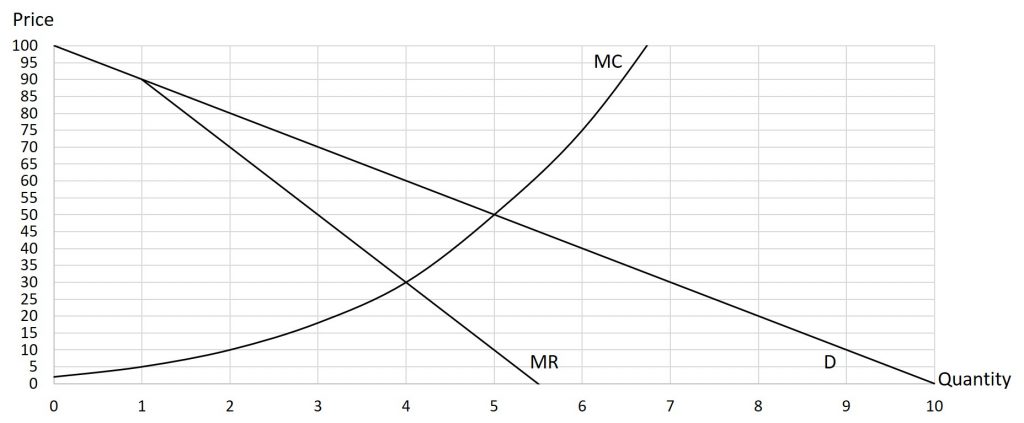
Solution: Q=4, P=$60
Problem 8.3.6: Use the graph below to determine the profit-maximizing price and output for the monopolist.
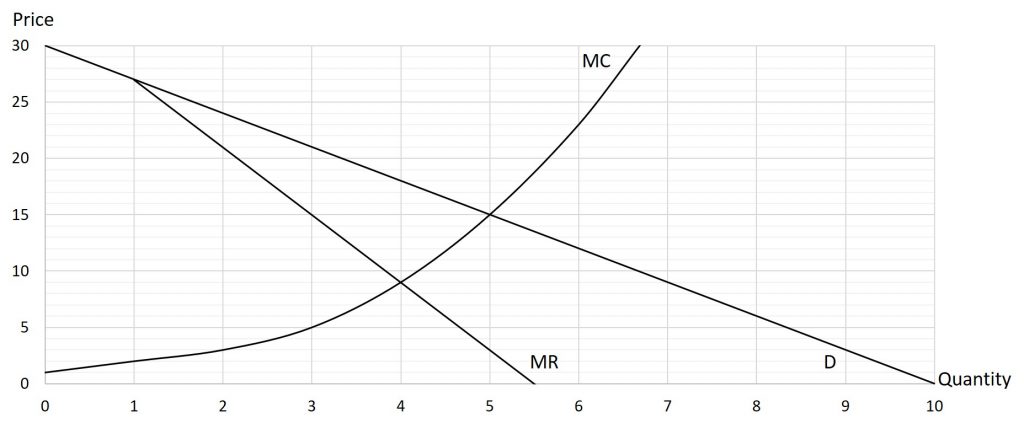
Solution: Q=4, P=$18
External Resources
Khan Academy: Types of Competition and Marginal Revenue
Khan Academy: Marginal Revenue and Marginal Cost in Imperfect Competition
Khan Academy: Economic Profit for a Monopoly
Khan Academy: Monopolist Optimizing Price – Revenue
Khan Academy: Monopolist Optimizing Price – Marginal Revenue
Khan Academy: Review of Revenue and Cost Graphs for a Monopoly
8.4 The power and inefficiency of monopoly
Review Activities
Problems
Problem 8.4.1: Consider the market given below:
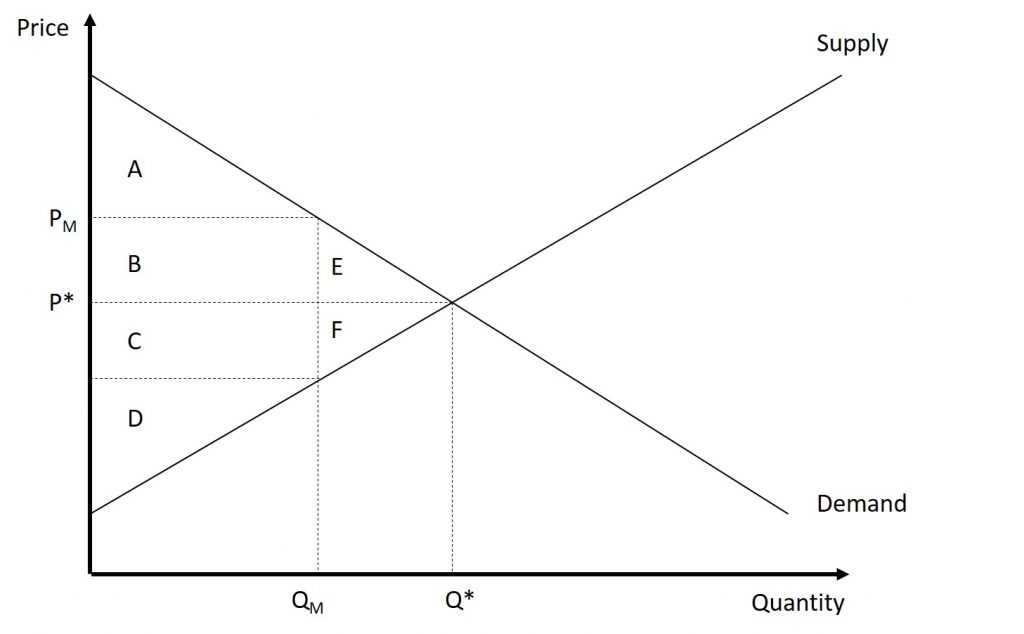
- What is the consumer surplus, producer surplus, total welfare, and deadweight loss when the market is in equilibrium.
- What is the consumer surplus, producer surplus, total welfare, and deadweight loss when a monopolist controls the market?
- How much consumer surplus was lost to the producers? How much consumer surplus was lost to the inefficiency of the market?
- How much producer surplus was transferred from the consumers? How much producer surplus was lost to the inefficiency of the market?
Solutions: CS=A+B+E, PS=C+D+F, TW=A+B+C+D+E+F, DWL=0; CS=A, PS=B+C+D, TW=A+B+C+D, DWL=E+F; Area B was consumer surplus but became producer surplus, Area E was consumer surplus but became DWL; Area B was consumer surplus that was transferred to producers and became producer surplus; producers lost area F to the inefficiency of the market.
Problem 8.4.2: Calculate the Lerner Index for the following situations. In addition, calculate the elasticity of demand.
- P=$3, MC=$2
- P=$6, MC=$6
- P=$15, MC=$3
Solutions: LI=0.33, εD=-3; LI=0 εD=-∞; LI=0.8 εD=-1.25
External Resources
Khan Academy: Monopolist Optimizing Price – Deadweight Loss
8.5 price discrimination
Review Activities
Problems
Problem 8.5.1: Suppose a monopolist faces the following demand schedule. Further, assume the marginal cost of production is constant at $10. Complete the tables below for both a single-price monopolist and a price discriminating monopolist.
Single-Price Monopolist
| Q | P | TR | TC | Tπ |
| 5 | 14 | |||
| 10 | 12 | |||
| 15 | 10 | |||
| 20 | 8 |
Price Discriminator
| Q | P | TR | TC | Tπ |
| 5 | 14 | |||
| 10 | 12 | |||
| 15 | 10 | |||
| 20 | 8 |
Solutions: See video for tables. For a single-price monopolist, greatest possible profit is $20. For a price discriminator, greatest possible profit is $30.
External Resources
Khan Academy: Price Discrimination
Khan Academy: Monopoly Price Discrimination

