Executive Summary
In 2009, The Building Information Modeling (BIM) Project Execution Planning Guide was released to support project teams by leading them through a planning process for BIM. A core principle of the planning procedure was to ‘Begin with the End in Mind’. This principle, when applied to the Architectural, Engineering, Construction, and Operations (AECO) Industry highlights the need for facility owners to understand and communicate their goals for implementing BIM throughout the lifecycle of the facility so that teams can produce the information during a project that will add value to the owner’s business operations. When the BIM Project Execution Planning Guide was released, few owners had outlined their BIM strategy for implementation – both within the operations of their facilities and within the design and construction process. Therefore, this Guide was developed to aid facility owners as they develop strategic, implementation, and procurement plans for BIM integrating into their organizations.
Facility owners should have a different outlook on the value of BIM for their projects. The BIM Project Execution Planning Guide was focused on streamlining the planning and implementation of BIM use within one capital facility or project. The value of BIM tools and processes for owners can be very much attuned to the tools and enabled processes within a given project, or it can differ with a focus on the facility operations and related data after complete. The BIM Planning Guide for Facility Owners seeks to facilitate an owner’s review and planning for the proper investment in BIM in line with the specific project focal points or strategic business interests, in addition to improving the value in delivering a single facility.
This Guide presents a structured approach to effectively plan the integration of BIM within an organization. Three planning procedures are presented:
• STRATEGIC PLANNING to assess existing organizational conditions; align BIM goals and objectives with desired BIM Uses and maturity level; and develop a transition plan for BIM implementation;
• IMPLEMENTATION PLANNING to develop the detailed implementation plan within the operations of the organization; and
• PROCUREMENT PLANNING to identify key issues to consider when creating BIM contract requirements.
The BIM Planning Elements
Throughout all stages of this Guide, there are six core “BIM Planning Elements” that must be considered. The BIM Planning Elements are as follows:
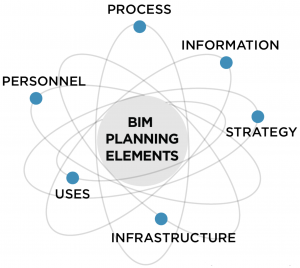
Figure 1-1: The BIM Planning Elements
1. STRATEGY
Defines the BIM goals and objectives; assesses change readiness; and considers management and resource support.
2. BIM USES
Identifies the methods in which BIM will be implemented for generating, processing, communicating, executing, and managing information about the owner’s facilities.
3. PROCESS
Describes the means to accomplish the BIM Uses by documenting the current methods, designing new processes leveraging BIM, and developing transition plans
4. INFORMATION
Documents the information needs of the organization, including the model element breakdown, level of development, and facility data.
5. INFRASTRUCTURE
Determines the technology infrastructure to support BIM including computer software, hardware, networks, and physical workspaces.
6. PERSONNEL
Establishes the roles, responsibilities, education, and training of the active participants in the BIM processes established.
Strategic Planning
The Strategic Planning procedure provides steps that an owner can use to plan for BIM at an organizational level. The purpose of this planning procedure is to allow you as an owner to determine your BIM goals and objectives and establish a road map to document how you will accomplish the goals and objectives. The Procedure includes:
- ASSESS the organization’s current internal and external level of BIM integration;
- ALIGN the organization’s BIM goals by identifying desired levels of maturity for BIM Uses; and
- ADVANCE the BIM maturity level through the development of a defined advancement strategy.
Implementation Planning
After the Strategic Plan has been developed, Implementation Planning can begin. The purpose of this step is to determine and document the detailed guidelines and protocols for implementation. An Implementation Plan will include the following:
- PROCESS maps that clearly define how BIM will be integrated into the organization’s practices;
- INFORMATION requirements to support the implementation of BIM;
- TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE needed to support the process; and
- EDUCATION AND TRAINING for the personnel who will interact with BIM or resulting data.
Procurement Planning
Prior to the start of a facility project (new construction or renovation); an owner should develop contract requirements for BIM. These contract requirements are necessary to ensure that the owner’s BIM needs are met, and the entire project team has a common understanding of the requirements. It also supports the successful implementation of BIM throughout the lifecycle of the facility. With the proper documentation in place at the beginning of the project, the team can plan an effective BIM process for both the project and your needs. Core procurement components include:
- TEAM SELECTION CRITERIA to enable the procurement of qualified items;
- CONTRACT REQUIREMENTS to clearly define the BIM deliverables; and
- STANDARD BIM PROJECT EXECUTION PLAN TEMPLATE to initiate the detailed BIM planning process for a project

