16.4 Free Energy
Learning Objectives
- Define Gibbs free energy, and describe its relation to spontaneity
- Calculate free energy change for a process using free energies of formation for its reactants and products
- Calculate free energy change for a process using enthalpies of formation and the entropies for its reactants and products
- Explain how temperature affects the spontaneity of some processes
- Relate standard free energy changes to equilibrium constants
One of the challenges of using the second law of thermodynamics to determine if a process is spontaneous is that we must determine the entropy change for the system and the entropy change for the surroundings. An alternative approach involving a new thermodynamic property defined in terms of system properties only was introduced in the late nineteenth century by American mathematician Josiah Willard Gibbs. This new property is called the Gibbs free energy change (G) (or simply the free energy), and it is defined in terms of a system’s enthalpy and entropy as the following:
Free energy is a state function, and at constant temperature and pressure, the standard free energy change (ΔG°) may be expressed as the following:
(For simplicity’s sake, the subscript “sys” will be omitted henceforth.)
We can understand the relationship between this system property and the spontaneity of a process by recalling the previously derived second law expression:
The first law requires that qsurr = −qsys, and at constant pressure qsys = ΔH, and so this expression may be rewritten as the following:
ΔH is the enthalpy change of the system. Multiplying both sides of this equation by −T, and rearranging yields the following:
Comparing this equation to the previous one for free energy change shows the following relation:
The free energy change is therefore a reliable indicator of the spontaneity of a process, being directly related to the previously identified spontaneity indicator, ΔSuniv. Table 3 summarizes the relation between the spontaneity of a process and the arithmetic signs of these indicators.
| ΔSuniv > 0 | ΔG < 0 | spontaneous |
| ΔSuniv < 0 | ΔG > 0 | nonspontaneous |
| ΔSuniv = 0 | ΔG = 0 | reversible (at equilibrium) |
| Table 3. Relation between Process Spontaneity and Signs of Thermodynamic Properties | ||
Calculating Free Energy Change
Free energy is a state function, so its value depends only on the conditions of the initial and final states of the system that have undergone some change. A convenient and common approach to the calculation of free energy changes for physical and chemical reactions is by use of widely available compilations of standard state thermodynamic data. One method involves the use of standard enthalpies and entropies to compute standard free energy changes according to the following relation as demonstrated in Example 1.
Example 1
Evaluation of ΔG° Change from ΔH° and ΔS°
Use standard enthalpy and entropy data from Appendix G to calculate the standard free energy change for the vaporization of water at room temperature (298 K). What does the computed value for ΔG° say about the spontaneity of this process?
Solution
The process of interest is the following:
The standard change in free energy may be calculated using the following equation:
From Appendix G, here is the data:
| Substance | [latex]{\Delta}H_{\text{f}}^{\circ}(\text{kJ/mol})[/latex] | [latex]S_{298}^{\circ}(\text{J/K}{\cdot}\text{mol})[/latex] |
|---|---|---|
| H2O(l) | −286.83 | 70.0 |
| H2O(g) | −241.82 | 188.8 |
| Table 4. | ||
Combining at 298 K:
Converting everything into kJ and combining at 298 K:
At 298 K (25 °C) [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}\$ > 0, and so boiling is nonspontaneous (not spontaneous).
[h5p id="58"]
Free energy changes may also use the standard free energy of formation ([/latex]latex {\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}$), for each of the reactants and products involved in the reaction. The standard free energy of formation is the free energy change that accompanies the formation of one mole of a substance from its elements in their standard states. Similar to the standard enthalpies of formation, [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}[/latex] is by definition zero for elemental substances under standard state conditions. The approach to computing the free energy change for a reaction using this approach is the same as that demonstrated previously for enthalpy and entropy changes. For the reaction
the standard free energy change at room temperature may be calculated as
Example 2
Calculation of [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex]
Consider the decomposition of yellow mercury(II) oxide.
Calculate the standard free energy change at room temperature, [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex], using (a) standard free energies of formation and (b) standard enthalpies of formation and standard entropies. Do the results indicate the reaction to be spontaneous or nonspontaneous under standard conditions?
Solution
The required data are available in Appendix G and are shown here.
| Compound | [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}(\text{kJ/mol})[/latex] | [latex]{\Delta}H_{\text{f}}^{\circ}(\text{kJ/mol})[/latex] | [latex]S_{298}^{\circ}(\text{J/K}{\cdot}\text{mol})[/latex] |
|---|---|---|---|
| HgO (s, yellow) | −58.43 | −90.46 | 71.13 |
| Hg(l) | 0 | 0 | 75.9 |
| O2(g) | 0 | 0 | 205.2 |
| Table 5. | |||
(a) Using free energies of formation:
(b) Using enthalpies and entropies of formation:
Both ways to calculate the standard free energy change at 25 °C give the same numerical value (to three significant figures), and both predict that the process is nonspontaneous (not spontaneous) at room temperature.
Temperature Dependence of Spontaneity
As was previously demonstrated in this chapter’s section on entropy, the spontaneity of a process may depend upon the temperature of the system. Phase transitions, for example, will proceed spontaneously in one direction or the other depending upon the temperature of the substance in question. Likewise, some chemical reactions can also exhibit temperature dependent spontaneities. To illustrate this concept, the equation relating free energy change to the enthalpy and entropy changes for the process is considered:
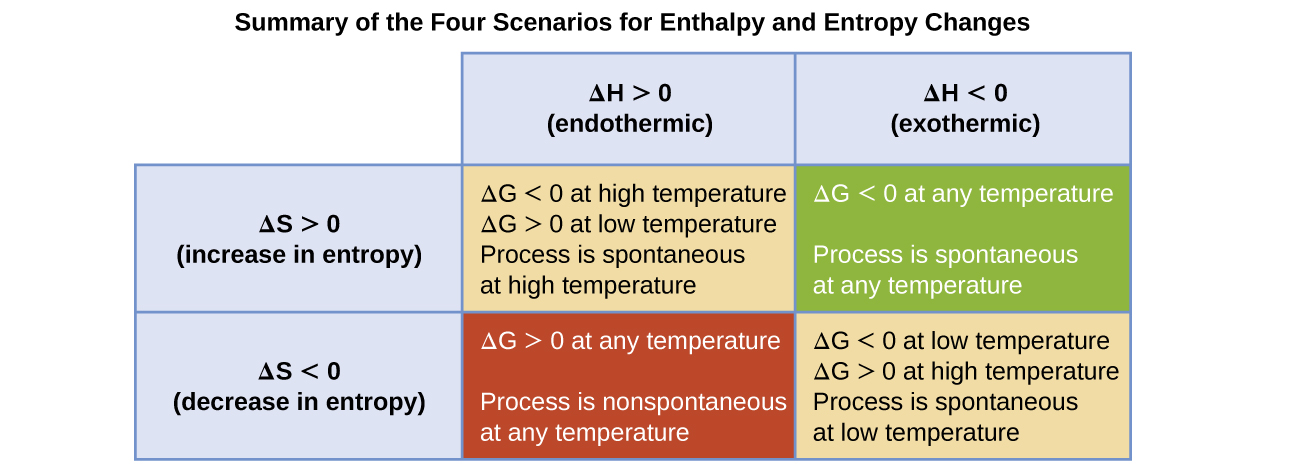
The spontaneity of a process, as reflected in the arithmetic sign of its free energy change, is then determined by the signs of the enthalpy and entropy changes and, in some cases, the absolute temperature. Since T is the absolute (kelvin) temperature, it can only have positive values. Four possibilities therefore exist with regard to the signs of the enthalpy and entropy changes:
- Both ΔH and ΔS are positive. This condition describes an endothermic process that involves an increase in system entropy. In this case, ΔG will be negative if the magnitude of the TΔS term is greater than ΔH. If the TΔS term is less than ΔH, the free energy change will be positive. Such a process is spontaneous at high temperatures and nonspontaneous at low temperatures.
- Both ΔH and ΔS are negative. This condition describes an exothermic process that involves a decrease in system entropy. In this case, ΔG will be negative if the magnitude of the TΔS term is less than ΔH. If the TΔS term’s magnitude is greater than ΔH, the free energy change will be positive. Such a process is spontaneous at low temperatures and nonspontaneous at high temperatures.
- ΔH is positive and ΔS is negative. This condition describes an endothermic process that involves a decrease in system entropy. In this case, ΔG will be positive regardless of the temperature. Such a process is nonspontaneous at all temperatures.
- ΔH is negative and ΔS is positive. This condition describes an exothermic process that involves an increase in system entropy. In this case, ΔG will be negative regardless of the temperature. Such a process is spontaneous at all temperatures.
These four scenarios are summarized in Figure 1.
Example 3
Predicting the Temperature Dependence of Spontaneity
The incomplete combustion of carbon is described by the following equation:
How does the spontaneity of this process depend upon temperature?
Solution
Combustion processes are exothermic (ΔH < 0). This particular reaction involves an increase in entropy due to the accompanying increase in the amount of gaseous species (net gain of one mole of gas, ΔS > 0). The reaction is therefore spontaneous (ΔG < 0) at all temperatures.
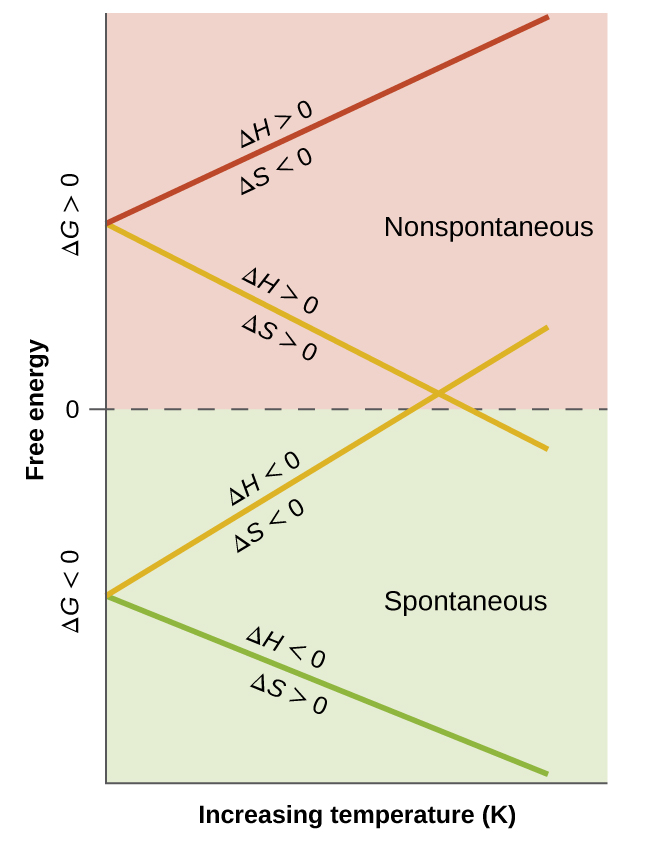
When considering the conclusions drawn regarding the temperature dependence of spontaneity, it is important to keep in mind what the terms “high” and “low” mean. Since these terms are adjectives, the temperatures in question are deemed high or low relative to some reference temperature. A process that is nonspontaneous at one temperature but spontaneous at another will necessarily undergo a change in “spontaneity” (as reflected by its ΔG) as temperature varies. This is clearly illustrated by a graphical presentation of the free energy change equation, in which ΔG is plotted on the y axis versus T on the x axis:
Such a plot is shown in Figure 2. A process whose enthalpy and entropy changes are of the same arithmetic sign will exhibit a temperature-dependent spontaneity as depicted by the two yellow lines in the plot. Each line crosses from one spontaneity domain (positive or negative ΔG) to the other at a temperature that is characteristic of the process in question. This temperature is represented by the x-intercept of the line, that is, the value of T for which ΔG is zero:
And so, saying a process is spontaneous at “high” or “low” temperatures means the temperature is above or below, respectively, that temperature at which ΔG for the process is zero. As noted earlier, this condition describes a system at equilibrium.
Example 4
Equilibrium Temperature for a Phase Transition
As defined in the chapter on liquids and solids, the boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which its solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium (that is, when vaporization and condensation occur at equal rates). Use the information in Appendix G to estimate the boiling point of water.
Solution
The process of interest is the following phase change:
When this process is at equilibrium, ΔG = 0, so the following is true:
Using the standard thermodynamic data from Appendix G,
The accepted value for water’s normal boiling point is 373.2 K (100.0 °C), and so this calculation is in reasonable agreement. Note that the values for enthalpy and entropy changes data used were derived from standard data at 298 K (Appendix G). If desired, you could obtain more accurate results by using enthalpy and entropy changes determined at (or at least closer to) the actual boiling point.
Free Energy and Equilibrium
The free energy change for a process may be viewed as a measure of its driving force. A negative value for ΔG represents a finite driving force for the process in the forward direction, while a positive value represents a driving force for the process in the reverse direction. When ΔG is zero, the forward and reverse driving forces are equal, and so the process occurs in both directions at the same rate (the system is at equilibrium).
In the chapter on equilibrium the reaction quotient, Q, was introduced as a convenient measure of the status of an equilibrium system. Recall that Q is the numerical value of the mass action expression for the system, and that you may use its value to identify the direction in which a reaction will proceed in order to achieve equilibrium. When Q is lesser than the equilibrium constant, K, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction until equilibrium is reached and Q = K. Conversely, if Q < K, the process will proceed in the reverse direction until equilibrium is achieved.
The free energy change for a process taking place with reactants and products present under nonstandard conditions, ΔG, is related to the standard free energy change, ΔG°, according to this equation:
R is the gas constant (8.314 J/K mol), T is the kelvin or absolute temperature, and Q is the reaction quotient. We may use this equation to predict the spontaneity for a process under any given set of conditions as illustrated in Example 5.
Example 5
Calculating ΔG under Nonstandard Conditions
What is the free energy change for the process shown here under the specified conditions?
T = 25 °C, [latex]\text{P}_{\text{N}_2} = 0.870\;\text{atm}[/latex], [latex]\text{P}_{\text{H}_2} = 0.250\;\text{atm}[/latex], and [latex]\text{P}_{\text{NH}_3} = 12.9\;\text{atm}[/latex]
Solution
The equation relating free energy change to standard free energy change and reaction quotient may be used directly:
Since the computed value for ΔG is positive, the reaction is nonspontaneous under these conditions.
For a system at equilibrium, Q = K and ΔG = 0, and the previous equation may be written as
This form of the equation provides a useful link between these two essential thermodynamic properties, and it can be used to derive equilibrium constants from standard free energy changes and vice versa. The relations between standard free energy changes and equilibrium constants are summarized in Table 6.
| K | ΔG° | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| > 1 | < 0 | Products are more abundant at equilibrium. |
| < 1 | > 0 | Reactants are more abundant at equilibrium. |
| = 1 | = 0 | Reactants and products are equally abundant at equilibrium. |
| Table 6. Relations between Standard Free Energy Changes and Equilibrium Constants | ||
Example 6
Calculating an Equilibrium Constant using Standard Free Energy Change
Given that the standard free energies of formation of Ag+(aq), Cl−(aq), and AgCl(s) are 77.1 kJ/mol, −131.2 kJ/mol, and −109.8 kJ/mol, respectively, calculate the solubility product, Ksp, for AgCl.
Solution
The reaction of interest is the following:
The standard free energy change for this reaction is first computed using standard free energies of formation for its reactants and products:
The equilibrium constant for the reaction may then be derived from its standard free energy change:
This result is in reasonable agreement with the value provided in Appendix J.
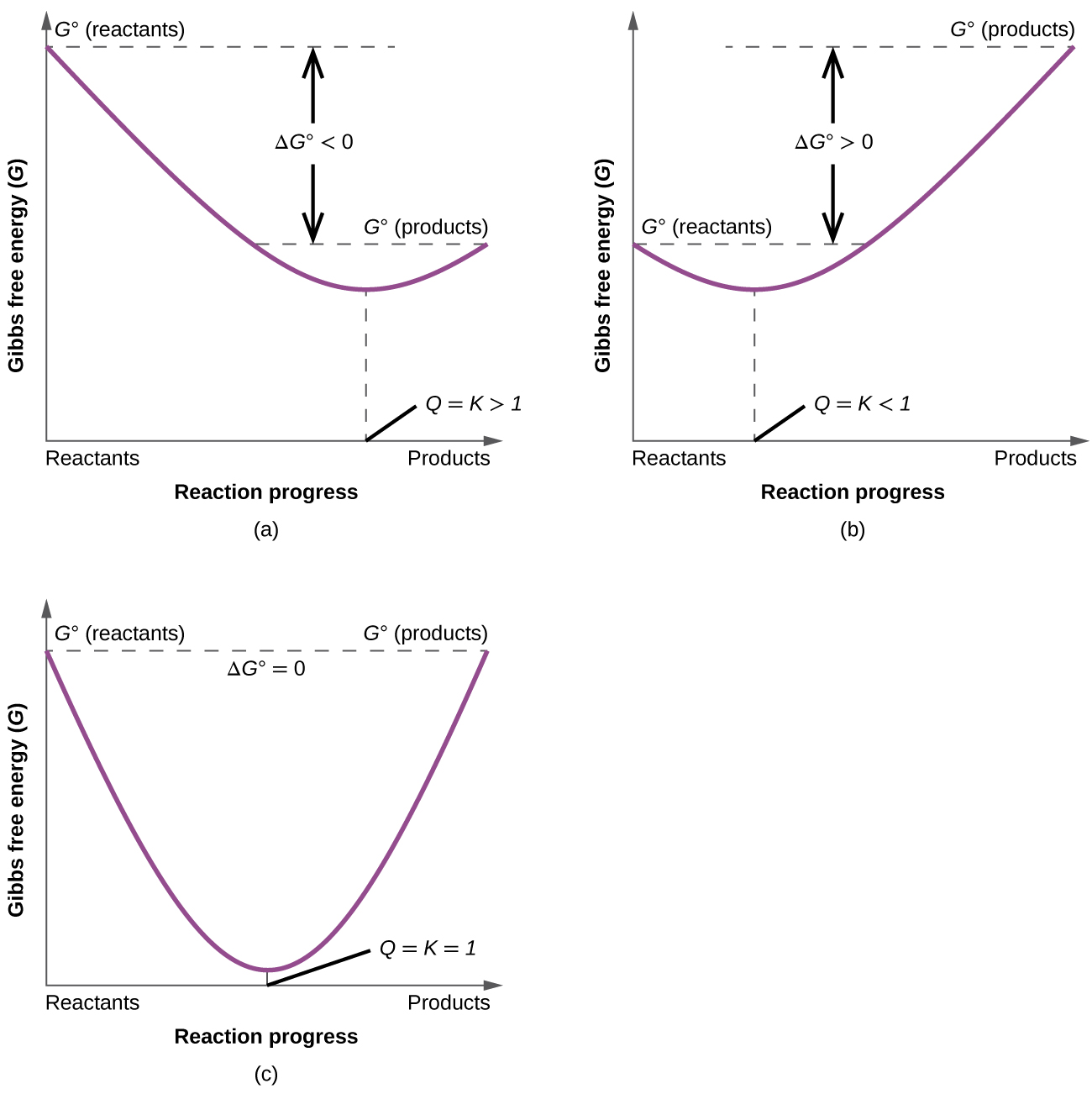
To further illustrate the relation between these two essential thermodynamic concepts, consider the observation that reactions spontaneously proceed in a direction that ultimately establishes equilibrium. As may be shown by plotting the free energy change versus the extent of the reaction (for example, as reflected in the value of Q), equilibrium is established when the system’s free energy is minimized (Figure 3). If a system is present with reactants and products present in nonequilibrium amounts (Q ≠ K), the reaction will proceed spontaneously in the direction necessary to establish equilibrium.
Key Concepts and Summary
Gibbs free energy (G) is a state function defined with regard to system quantities only and may be used to predict the spontaneity of a process. A negative value for ΔG indicates a spontaneous process; a positive ΔG indicates a nonspontaneous process; and a ΔG of zero indicates that the system is at equilibrium. A number of approaches to the computation of free energy changes are possible.
Key Equations
- ΔG = ΔH − TΔS
- ΔG = ΔG° + RT ln Q
- ΔG° = −RT ln K
Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises
- What is the difference between ΔG, ΔG°, and [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] for a chemical change?
- A reactions has [latex]{\Delta}H_{298}^{\circ} = 100\;\text{kJ/mol}[/latex] and [latex]{\Delta}S_{298}^{\circ} = 250\;\text{J/mol}{\cdot}\text{K}[/latex]. Is the reaction spontaneous at room temperature? If not, under what temperature conditions will it become spontaneous?
- Explain what happens as a reaction starts with ΔG < 0 (negative) and reaches the point where ΔG = 0.
- Use the standard free energy of formation data in Appendix G to determine the free energy change for each of the following reactions, which are run under standard state conditions and 25 °C. Identify each as either spontaneous or nonspontaneous at these conditions.
(a) [latex]\text{MnO}_2(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Mn}(s)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{H}_2(g)\;+\;\text{Br}_2(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{HBr}(g)[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{Cu}(s)\;+\;\text{S}(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CuS}(s)[/latex]
(d) [latex]2\text{LiOH}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Li}_2\text{CO}_3(s)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{CH}_4(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{C}(s\text{,\;graphite})\;+\;2\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)[/latex]
(f) [latex]\text{CS}_2(g)\;+\;3\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CCl}_4(g)\;+\;\text{S}_2\text{Cl}_2(g)[/latex]
- Use the standard free energy data in Appendix G to determine the free energy change for each of the following reactions, which are run under standard state conditions and 25 °C. Identify each as either spontaneous or nonspontaneous at these conditions.
(a) [latex]\text{C}(s\text{,\;graphite})\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CO}_2(g)[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{O}_2(g)\;+\;\text{N}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{NO}(g)[/latex]
(c) [latex]2\text{Cu}(s)\;+\;\text{S}(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Cu}_2\text{S}(s)[/latex]
(d) [latex]\text{CaO}(s)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Ca(OH)}_2(s)[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3(s)\;+\;3\text{CO}(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{Fe}(s)\;+\;3\text{CO}_2(g)[/latex]
(f) [latex]\text{CaSO}_4\;{\cdot}\;2\text{H}_2\text{O}(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CaSO}_4(s)\;+\;2\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)[/latex]
- Given:
[latex]\begin{array}{ll} \text{P}_4(s)\;+\;5\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{P}_4\text{O}_{10}(s) & {\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -2697.0\;\text{kJ/mol} \\[0.5em] 2\text{H}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{H}_2\text{O}(g) & {\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -457.18\;\text{kJ/mol} \\[0.5em] 6\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;+\;\text{P}_4\text{O}_{10}(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;4\text{H}_3\text{PO}_4(l) & {\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -428.66\;\text{kJ/mol} \end{array}[/latex](a) Determine the standard free energy of formation, [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}[/latex], for phosphoric acid.
(b) How does your calculated result compare to the value in Appendix G? Explain.
- Is the formation of ozone (O3(g)) from oxygen (O2(g)) spontaneous at room temperature under standard state conditions?
- Consider the decomposition of red mercury(II) oxide under standard state conditions.
[latex]2\text{HgO}(s\text{,\;red})\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{Hg}(l)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)[/latex](a) Is the decomposition spontaneous under standard state conditions?
(b) Above what temperature does the reaction become spontaneous?
- Among other things, an ideal fuel for the control thrusters of a space vehicle should decompose in a spontaneous exothermic reaction when exposed to the appropriate catalyst. Evaluate the following substances under standard state conditions as suitable candidates for fuels.
(a) Ammonia: [latex]2\text{NH}_3(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{N}_2(g)\;+\;3\text{H}_2(g)[/latex]
(b) Diborane: [latex]\text{B}_2\text{H}_6(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{B}(g)\;+\;3\text{H}_2(g)[/latex]
(c) Hydrazine: [latex]\text{N}_2\text{H}_4(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{N}_2(g)\;+\;2\text{H}_2(g)[/latex]
(d) Hydrogen peroxide: [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}_2(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;+\;\frac{1}{2}\text{O}_2(g)[/latex]
- Calculate ΔG° for each of the following reactions from the equilibrium constant at the temperature given.
(a) [latex]\text{N}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{NO}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 2000\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 4.1\;\times\;10^{-4}[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{H}_2(g)\;+\;\text{I}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{HI}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 400\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 50.0[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{CO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{H}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CO}(g)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 980\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 1.67[/latex]
(d) [latex]\text{CaCO}_3(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CaO}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 900\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 1.04[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{HF}(aq)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{H}_3\text{O}^{+}(aq)\;+\;\text{F}^{-}(aq)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 25\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 7.2\;\times\;10^{-4}[/latex]
(f) [latex]\text{AgBr}(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Ag}^{+}(aq)\;+\;\text{Br}^{-}(aq)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 25\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 3.3\;\times\;10^{-13}[/latex]
- Calculate ΔG° for each of the following reactions from the equilibrium constant at the temperature given.
(a) [latex]\text{Cl}_2(g)\;+\;\text{Br}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{BrCl}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 25\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 4.7\;\times\;10^{-2}[/latex]
(b) [latex]2\text{SO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\leftrightharpoons}\;2\text{SO}_3(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 500\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 48.2[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\rightleftharpoons}\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 60\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 0.196\;\text{atm}[/latex]
(d) [latex]\text{CoO}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}(g)\;{\rightleftharpoons}\;\text{Co}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 550\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 4.90\;\times\;10^2[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{CH}_3\text{NH}_2(aq)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CH}_3\text{NH}_3^{+}(aq)\;+\;\text{OH}^{-}(aq)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 25\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 4.4\;\times\;10^{-4}[/latex]
(f) [latex]\text{PbI}_2(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Pb}^{2+}(aq)\;+\;2\text{I}^{-}(aq)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\text{T} = 25\;^{\circ}\text{C}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{p}} = 8.7\;\times\;10^{-9}[/latex]
- Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 °C for each of the following reactions from the value of ΔG° given.
(a) [latex]\text{O}_2(g)\;+\;2\text{F}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{OF}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -9.2\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{I}_2(s)\;+\;\text{Br}_2(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{IBr}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = 7.3\;\text{kJI}[/latex]
(c) [latex]2\text{LiOH}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Li}_2\text{CO}_3(s)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -79\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(d) [latex]\text{N}_2\text{O}_3(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NO}(g)\;+\;\text{NO}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -1.6\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{SnCl}_4(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{SnCl}_4(l)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = 8.0\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
- Calculate the equilibrium constant at 25 °C for each of the following reactions from the value of ΔG° given.
(a) [latex]\text{I}_2(s)\;+\;\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{ICl}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -10.88\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{H}_2(g)\;+\;\text{I}_2(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{HI}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = 3.4\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{CS}_2(g)\;+\;3\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CCl}_4(g)\;+\;\text{S}_2\text{Cl}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -39\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(d) [latex]2\text{SO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{SO}_3(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -141.82\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{CS}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CS}_2(l)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G^{\circ} = -1.88\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
- Calculate the equilibrium constant at the temperature given.
(a) [latex]\text{O}_2(g)\;+\;2\text{F}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{F}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 100\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{I}_2(s)\;+\;\text{Br}_2(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{IBr}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 0.0\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(c) [latex]2\text{LiOH}(s)\;+\;\text{CO}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Li}_2\text{CO}_3(s)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 575\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(d) [latex]\text{N}_2\text{O}_3(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NO}(g)\;+\;\text{NO}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = -10.0\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{SnCl}_4(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{SnCl}_4(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 200\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
- Calculate the equilibrium constant at the temperature given.
(a) [latex]\text{I}_2(s)\;+\;\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{ICl}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 100\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{H}_2(g)\;+\;\text{I}_2(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{HI}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 0.0\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{CS}_2(g)\;+\;3\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CCl}_4(g)\;+\;\text{S}_2\text{Cl}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 125\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(d) [latex]2\text{SO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{SO}_3(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 675\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
(e) [latex]\text{CS}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CS}_2(l)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(\text{T} = 90\;^{\circ}\text{C})[/latex]
- Consider the following reaction at 298 K:
[latex]\text{N}_2\text{O}_4(g)\;{\rightleftharpoons}\;2\text{NO}_2(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;K_{\text{P}} = 0.142[/latex]What is the standard free energy change at this temperature? Describe what happens to the initial system, where the reactants and products are in standard states, as it approaches equilibrium.
- Determine the normal boiling point (in kelvin) of dichloroethane, CH2Cl2. Find the actual boiling point using the Internet or some other source, and calculate the percent error in the temperature. Explain the differences, if any, between the two values.
- Under what conditions is [latex]\text{N}_2\text{O}_3(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NO}(g)\;+\;\text{NO}_2(g)[/latex] spontaneous?
- At room temperature, the equilibrium constant (Kw) for the self-ionization of water is 1.00 × 10−14. Using this information, calculate the standard free energy change for the aqueous reaction of hydrogen ion with hydroxide ion to produce water. (Hint: The reaction is the reverse of the self-ionization reaction.)
- Hydrogen sulfide is a pollutant found in natural gas. Following its removal, it is converted to sulfur by the reaction [latex]2\text{H}_2\text{S}(g)\;+\;\text{SO}_2(g)\;{\rightleftharpoons}\;\frac{3}{8}\text{S}_8(s\text{,\;rhombic})\;+\;2\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)[/latex]. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction? Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic?
- Consider the decomposition of CaCO3(s) into CaO(s) and CO2(g). What is the equilibrium partial pressure of CO2 at room temperature?
- In the laboratory, hydrogen chloride (HCl(g)) and ammonia (NH3(g)) often escape from bottles of their solutions and react to form the ammonium chloride (NH4Cl(s)), the white glaze often seen on glassware. Assuming that the number of moles of each gas that escapes into the room is the same, what is the maximum partial pressure of HCl and NH3 in the laboratory at room temperature? (Hint: The partial pressures will be equal and are at their maximum value when at equilibrium.)
- Benzene can be prepared from acetylene. [latex]3\text{C}_2\text{H}_2(g)\;{\rightleftharpoons}\;\text{C}_6\text{H}_6(g)[/latex]. Determine the equilibrium constant at 25 °C and at 850 °C. Is the reaction spontaneous at either of these temperatures? Why is all acetylene not found as benzene?
- Carbon dioxide decomposes into CO and O2 at elevated temperatures. What is the equilibrium partial pressure of oxygen in a sample at 1000 °C for which the initial pressure of CO2 was 1.15 atm?
- Carbon tetrachloride, an important industrial solvent, is prepared by the chlorination of methane at 850 K.
[latex]\text{CH}_4(g)\;+\;4\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{CCl}_4(g)\;+\;4\text{HCl}(g)[/latex]What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 850 K? Would the reaction vessel need to be heated or cooled to keep the temperature of the reaction constant?
- Acetic acid, CH3CO2H, can form a dimer, (CH3CO2H)2, in the gas phase.
[latex]2\text{CH}_3\text{CO}_2\text{H}(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;(\text{CH}_3\text{CO}_2\text{H})_2(g)[/latex]The dimer is held together by two hydrogen bonds with a total strength of 66.5 kJ per mole of dimer.
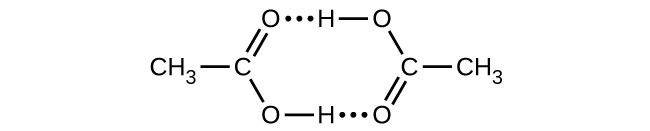
At 25 °C, the equilibrium constant for the dimerization is 1.3 × 103 (pressure in atm). What is ΔS° for the reaction?
- Nitric acid, HNO3, can be prepared by the following sequence of reactions:
[latex]4\text{NH}_3(g)\;+\;5\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;4\text{NO}(g)\;+\;6\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)[/latex]
[latex]2\text{NO}(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{NO}_2(g)[/latex]
[latex]3\text{NO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{HNO}_3(l)\;+\;\text{NO}(g)[/latex]How much heat is evolved when 1 mol of NH3(g) is converted to HNO3(l)? Assume standard states at 25 °C.
- Determine ΔG for the following reactions.
(a) Antimony pentachloride decomposes at 448 °C. The reaction is:
[latex]\text{SbCl}_5(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{SbCl}_3(g)\;+\;\text{Cl}_2(g)[/latex]
An equilibrium mixture in a 5.00 L flask at 448 °C contains 3.85 g of SbCl5, 9.14 g of SbCl3, and 2.84 g of Cl2.
(b) Chlorine molecules dissociate according to this reaction:
[latex]\text{Cl}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{Cl}(g)[/latex]
1.00% of Cl2 molecules dissociate at 975 K and a pressure of 1.00 atm.
- Given that the [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}[/latex] for Pb2+(aq) and Cl−(aq) is −24.3 kJ/mole and −131.2 kJ/mole respectively, determine the solubility product, Ksp, for PbCl2(s).
- Determine the standard free energy change, [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}[/latex], for the formation of S2−(aq) given that the [latex]{\Delta}G_{\text{f}}^{\circ}[/latex] for Ag+(aq) and Ag2S(s) are 77.1 k/mole and −39.5 kJ/mole respectively, and the solubility product for Ag2S(s) is 8 × 10−51.
- Determine the standard enthalpy change, entropy change, and free energy change for the conversion of diamond to graphite. Discuss the spontaneity of the conversion with respect to the enthalpy and entropy changes. Explain why diamond spontaneously changing into graphite is not observed.
- The evaporation of one mole of water at 298 K has a standard free energy change of 8.58 kJ.
[latex]\text{H}_2\text{O}(l)\;{\leftrightharpoons}\;\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = 8.58\;\text{kJ}[/latex](a) Is the evaporation of water under standard thermodynamic conditions spontaneous?
(b) Determine the equilibrium constant, KP, for this physical process.
(c) By calculating ∆G, determine if the evaporation of water at 298 K is spontaneous when the partial pressure of water, [latex]\text{P}_{\text{H}_2\text{O}}[/latex], is 0.011 atm.
(d) If the evaporation of water were always nonspontaneous at room temperature, wet laundry would never dry when placed outside. In order for laundry to dry, what must be the value of [latex]\text{P}_{\text{H}_2\text{O}}[/latex] in the air?
- In glycolysis, the reaction of glucose (Glu) to form glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) requires ATP to be present as described by the following equation:
[latex]\text{Glu}\;+\;\text{ATP}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{G}6\text{P}\;+\;\text{ADP}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -17\;\text{kJ}[/latex]In this process, ATP becomes ADP summarized by the following equation:
[latex]\text{ATP}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{ADP}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -30\;\text{kJ}[/latex]
Determine the standard free energy change for the following reaction, and explain why ATP is necessary to drive this process:
[latex]\text{Glu}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{G}6\text{P}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = \text{?}[/latex]
- One of the important reactions in the biochemical pathway glycolysis is the reaction of glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) to form fructose-6-phosphate (F6P):
[latex]\text{G}6\text{P}\;{\leftrightharpoons}\;\text{F}6\text{P}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = 1.7\;\text{kJ}[/latex](a) Is the reaction spontaneous or nonspontaneous under standard thermodynamic conditions?
(b) Standard thermodynamic conditions imply the concentrations of G6P and F6P to be 1 M, however, in a typical cell, they are not even close to these values. Calculate ΔG when the concentrations of G6P and F6P are 120 μM and 28 μM respectively, and discuss the spontaneity of the forward reaction under these conditions. Assume the temperature is 37 °C.
- Without doing a numerical calculation, determine which of the following will reduce the free energy change for the reaction, that is, make it less positive or more negative, when the temperature is increased. Explain.
(a) [latex]\text{N}_2(g)\;+\;3\text{H}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;2\text{NH}_3(g)[/latex]
(b) [latex]\text{HCl}(g)\;+\;\text{NH}_3(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NH}_4\text{Cl}(s)[/latex]
(c) [latex](\text{NH}_4)_2\text{Cr}_2\text{O}_7(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Cr}_2\text{O}_3(s)\;+\;4\text{H}_2\text{O}(g)\;+\;\text{N}_2(g)[/latex]
(d) [latex]2\text{Fe}(s)\;+\;3\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Fe}_2\text{O}_3(s)[/latex]
- When ammonium chloride is added to water and stirred, it dissolves spontaneously and the resulting solution feels cold. Without doing any calculations, deduce the signs of ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS for this process, and justify your choices.
- An important source of copper is from the copper ore, chalcocite, a form of copper(I) sulfide. When heated, the Cu2S decomposes to form copper and sulfur described by the following equation:
[latex]\text{Cu}_2\text{S}(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Cu}(s)\;+\;\text{S}(s)[/latex](a) Determine [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] for the decomposition of Cu2S(s).
(b) The reaction of sulfur with oxygen yields sulfur dioxide as the only product. Write an equation that describes this reaction, and determine [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] for the process.
(c) The production of copper from chalcocite is performed by roasting the Cu2S in air to produce the Cu. By combining the equations from Parts (a) and (b), write the equation that describes the roasting of the chalcocite, and explain why coupling these reactions together makes for a more efficient process for the production of the copper.
- What happens to [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] (becomes more negative or more positive) for the following chemical reactions when the partial pressure of oxygen is increased?
(a) [latex]\text{S}(s)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{SO}_2(g)[/latex]
(b) [latex]2\text{SO}_2(g)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{SO}_3(g)[/latex]
(c) [latex]\text{HgO}(s)\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Hg}(l)\;+\;\text{O}_2(g)[/latex]
Glossary
- Gibbs free energy change (G)
- thermodynamic property defined in terms of system enthalpy and entropy; all spontaneous processes involve a decrease in G
- standard free energy change (ΔG°)
- change in free energy for a process occurring under standard conditions (1 bar pressure for gases, 1 M concentration for solutions)
- standard free energy of formation [latex](\Delta G^{^circ}_{\text{f}}[/latex]
- change in free energy accompanying the formation of one mole of substance from its elements in their standard states
Solutions
Answers to Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises
2. The reaction is nonspontaneous at room temperature.
Above 400 K, ΔG will become negative, and the reaction will become spontaneous.
4. (a) 465.1 kJ nonspontaneous; (b) −106.86 kJ spontaneous; (c) −53.6 kJ spontaneous; (d) −83.4 kJ spontaneous; (e) −406.7 kJ spontaneous; (f) −30.0 kJ spontaneous
6. (a) −1124.3 kJ/mol for the standard free energy change. (b) The calculation agrees with the value in Appendix G because free energy is a state function (just like the enthalpy and entropy), so its change depends only on the initial and final states, not the path between them.
8. (a) The reaction is nonspontaneous; (b) Above 566 °C the process is spontaneous.
10. (a) 1.5 × 102 kJ; (b) −21.9 kJ; (c) −5.34 kJ; (d) −0.383 kJ; (e) 18 kJ; (f) 71 kJ
12. (a) K = 41; (b) K = 0.053; (c) K = 6.9 × 1013; (d) K = 1.9; (e) K = 0.04
14. In each of the following, the value of ΔG is not given at the temperature of the reaction. Therefore, we must calculate ΔG from the values ΔH° and ΔS and then calculate ΔG from the relation ΔG = ΔH° − TΔS°.
(a) K = 1.29;
(b) K = 2.51 × 10−3;
(c) K = 4.83 × 103;
(d) K = 0.219;
(e) K = 16.1
16. The standard free energy change is [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -RT\;\text{ln}\;K = 4.84\;\text{kJ/mol}[/latex]. When reactants and products are in their standard states (1 bar or 1 atm), Q = 1. As the reaction proceeds toward equilibrium, the reaction shifts left (the amount of products drops while the amount of reactants increases): Q < 1, and [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}[/latex] becomes less positive as it approaches zero. At equilibrium, Q = K, and ΔG = 0.
18. The reaction will be spontaneous at temperatures greater than 287 K.
20. K = 5.35 × 1015
The process is exothermic.
22. 1.0 × 10−8 atm. This is the maximum pressure of the gases under the stated conditions.
24. [latex]x = 1.29\;\times\;10^{-5}\;\text{atm} = \text{P}_{\text{O}_2}[/latex]
26. −0.16 kJ
28. (a) −22.1 kJ; (b) 61.6 kJ/mol
30. 90 kJ/mol
32. (a) Under standard thermodynamic conditions, the evaporation is nonspontaneous; (b) Kp = 0.031; (c) The evaporation of water is spontaneous; (d) [latex]\text{P}_{\text{H}_2\text{O}}[/latex] must always be less than Kp or less than 0.031 atm. 0.031 atm represents air saturated with water vapor at 25 °C, or 100% humidity.
34. (a) Nonspontaneous as [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}\;{\textgreater}\;0[/latex]; (b) [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ} = -RT\;\text{ln}\;K\text{,\;}{\Delta}G = 1.7\;\times\;10^3\;+\;(8.314\;\times\;335\;\times\;\text{ln}\;\frac{28}{128}) = -2.5\;\text{kJ}[/latex]. The forward reaction to produce F6P is spontaneous under these conditions.
36. ΔG is negative as the process is spontaneous. ΔH is positive as with the solution becoming cold, the dissolving must be endothermic. ΔS must be positive as this drives the process, and it is expected for the dissolution of any soluble ionic compound.
38. (a) Increasing [latex]P_{\text{O}_2}[/latex] will shift the equilibrium toward the products, which increases the value of K. [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] therefore becomes more negative.
(b) Increasing [latex]P_{\text{O}_2}[/latex] will shift the equilibrium toward the products, which increases the value of K. [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] therefore becomes more negative.
(c) Increasing [latex]P_{\text{O}_2}[/latex] will shift the equilibrium the reactants, which decreases the value of K. [latex]{\Delta}G_{298}^{\circ}[/latex] therefore becomes more positive.

