Hydrolysis of Salts (14.4)
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Predict whether a salt solution will be acidic, basic, or neutral
- Calculate the concentrations of the various species in a salt solution
- Describe the acid ionization of hydrated metal ions
Salts with Acidic Ions
Salts are ionic compounds composed of cations and anions, either of which may be capable of undergoing an acid or base ionization reaction with water. Aqueous salt solutions, therefore, may be acidic, basic, or neutral, depending on the relative acid-base strengths of the salt's constituent ions. For example, dissolving ammonium chloride in water results in its dissociation, as described by the equation
NH4 Cl(s) ⇌ NH4 + (aq) + Cl− (aq)
The ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of the weak base ammonia, NH3, and so it will undergo acid ionization (or acid hydrolysis):
NH4 +(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + NH3(aq)
Salts are ionic compounds composed of cations and anions, either of which may be capable of undergoing an acid or base ionization reaction with water. Aqueous salt solutions, therefore, may be acidic, basic, or neutral, depending on the relative acid-base strengths of the salt’s constituent ions. For example, dissolving the ammonium chloride in water results in its dissociation, as described by the equation
NH4 Cl(s) ⇌ NH4 + (aq) + Cl− (aq)
The ammonium ion is the conjugate acid of the base ammonia, NH3; its acid ionization (or acid hydrolysis) reaction is represented by
NH4 +(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + NH3(aq) Ka = Kw/Kb
Since ammonia is a weak base, Kb is measurable and Ka > 0 (ammonium ion is a weak acid).
The chloride ion is the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid, and so its base ionization (or base hydrolysis) reaction is represented by
Cl− (aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCl(aq) + OH− (aq) Kb = Kw/Ka
Since HCl is a strong acid, Ka is immeasurably large and Kb ≈ 0 (chloride ions don’t undergo appreciable hydrolysis).
Example 14.15
Calculating the pH of an Acidic Salt Solution
Thus, dissolving ammonium chloride in water yields a solution of weak acid cations ( NH4 + ) and inert anions (Cl−), resulting in an acidic solution.
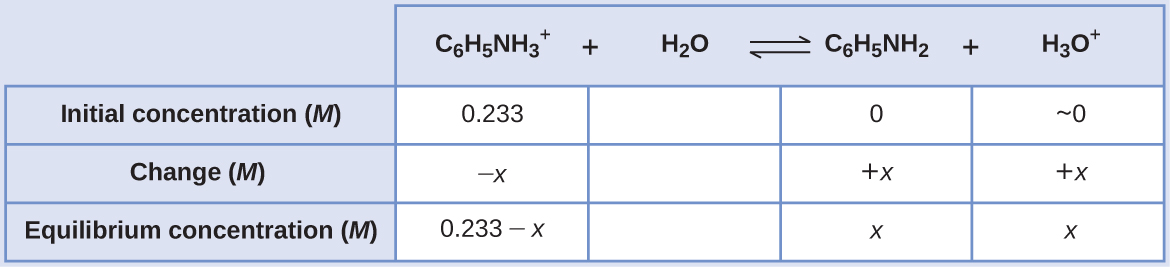
Aniline is an amine that is used to manufacture dyes. It is isolated as anilinium chloride, [C6H5NH3 +] Cl, a salt prepared by the reaction of the weak base aniline and hydrochloric acid. What is the pH of a 0.233 M solution of anilinium chloride
C6H5NH3 +(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + C6H5NH2(aq)
Solution
The Ka for anilinium ion is derived from the Kb for its conjugate base, aniline (see Appendix H):
Ka = [latex]\frac{K_{w}}{K_{b}} = \frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{4.3 \times 10^{-10}} = 2.3 \times 10^{-5}[/latex]
Using the provided information, an ICE table for this system is prepared:
Substituting these equilibrium concentration terms into the Ka expression gives
Ka = [C6H5NH2][H3O+ ]/[C6H5NH3 + ]
2.3 × 10−5 = (x)(x)/0.233 − x)
Assuming x << 0.233, the equation is simplified and solved for x:
2.3 × 10−5 = x2/0.233x = 0.0023 M
The ICE table defines x as the hydronium ion molarity, and so the pH is computed as
pH = − log[H3O+ ] = −log(0.0023) = 2.64
Check Your Learning
What is the hydronium ion concentration in a 0.100-M solution of ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, a salt composed of the ions NH4 + and NO3 −. Which is the stronger acid C6H5NH3 + or NH4 + ?
Answer: [H3O+] = 7.5 × 10−6 M; C6H5NH3 + is the stronger acid.
Salts with Basic Ions
As another example, consider dissolving sodium acetate in water:
NaCH3 CO2(s) Na + (aq) + CH3 CO2 −(aq)
The sodium ion does not undergo appreciable acid or base ionization and has no effect on the solution pH. This may seem obvious from the ion's formula, which indicates no hydrogen or oxygen atoms, but some dissolved metal ions function as weak acids, as addressed later in this section.
The acetate ion, CH3 CO2 − , is the conjugate base of acetic acid, CH3CO2H, and so its base ionization (or base hydrolysis) reaction is represented by
CH3CO2 − (aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3CO2 H(aq) + OH − (aq) Kb = Kw/Ka
Because acetic acid is a weak acid, its Ka is measurable and Kb > 0 (acetate ion is a weak base).
Dissolving sodium acetate in water yields a solution of inert cations (Na+) and weak base anions (CH3 CO2 − ), resulting in a basic solution.
Example 14.16
Equilibrium in a Solution of a Salt of a Weak Acid and a Strong Base
Determine the acetic acid concentration in a solution with [CH3 CO2 −] = 0.050 M and [OH−] = 2.5 × 10−6 M at equilibrium. The reaction is:
CH3 CO2 −(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CH3CO2 H(aq) + OH−(aq)
Solution
The provided equilibrium concentrations and a value for the equilibrium constant will permit calculation of the missing equilibrium concentration. The process in question is the base ionization of acetate ion, for which
Kb (for CH3CO2 −) = [latex]\frac{K_{w}}{K_{a} (\text{for} CH_{3}CO_{2}H)} = \frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{1.8 \times 10^{-5}}[/latex] = 5.6 x 10-10
Substituting the available values into the Kb expression gives
Kb = [latex]\frac{[CH_{3}CO_{2}H][OH^{-}]}{[CH_{3}CO_{2} ^{-}]}[/latex] = 5.6 x 10-10
= [latex]\frac{[CH_{3}CO_{2}H](2.5 \times 10^{-6})}{(0.050)}[/latex] = 5.6 x 10-6
Solving the above equation for the acetic acid molarity yields [CH3CO2H] = 1.1 × 10−5 M.
Check Your Learning
What is the pH of a 0.083-M solution of NaCN?
Answer: 11.11
Salts with Acidic and Basic Ions
Some salts are composed of both acidic and basic ions, and so the pH of their solutions will depend on the relative strengths of these two species. Likewise, some salts contain a single ion that is amphiprotic, and so the relative strengths of this ion’s acid and base character will determine its effect on solution pH. For both types of salts, a comparison of the Ka and Kb values allows prediction of the solution’s acid-base status, as illustrated in the following example exercise.
Example 14.17
Determining the Acidic or Basic Nature of Salts
Determine whether aqueous solutions of the following salts are acidic, basic, or neutral:
(a) KBr
(b) NaHCO3
(c) Na2HPO4
(d) NH4F
Solution
Consider each of the ions separately in terms of its effect on the pH of the solution, as shown here:
(a) The K+ cation is inert and will not affect pH. The bromide ion is the conjugate base of a strong acid, and so it is of negligible base strength (no appreciable base ionization). The solution is neutral.
(b) The Na+ cation is inert and will not affect the pH of the solution; while the HCO3 − anion is amphiprotic. The Ka of HCO3 − is 4.7 × 10−11,and its Kb is [latex]\frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{4.3 \times 10^{-7}}[/latex] = 2.3 x 10-8
Since Kb >> Ka, the solution is basic.
(c) The Na+ cation is inert and will not affect the pH of the solution, while the HPO4 2− anion is amphiprotic. The Ka of HPO4 2− is 4.2 × 10−13, and its Kb is [latex]\frac{1.0 \times 10^{-14}}{4.3 \times 10^{-7}}[/latex] = 1.6 x 10-7. Because Kb >> Ka, the solution is basic.
(d) The NH4 + ion is acidic (see above discussion) and the F− ion is basic (conjugate base of the weak acid HF). Comparing the two ionization constants: Ka of NH4 + is 5.6 × 10−10 and the Kb of F− is 1.4 × 10−11, so the solution is acidic, since Ka > Kb.
Check Your Learning
Determine whether aqueous solutions of the following salts are acidic, basic, or neutral:
(a) K2CO3
(b) CaCl2
(c) KH2PO4
(d) (NH4)2CO3
Answer: (a) basic; (b) neutral; (c) acidic; (d) basic
The Ionization of Hydrated Metal Ions
Unlike the group 1 and 2 metal ions of the preceding examples (Na+, Ca2+, etc.), some metal ions function as acids in aqueous solutions. These ions are not just loosely solvated by water molecules when dissolved, instead they are covalently bonded to a fixed number of water molecules to yield a complex ion (see chapter on coordination chemistry). As an example, the dissolution of aluminum nitrate in water is typically represented as
Al(NO3)(s) ⇌ Al3 + (aq) + 3NO3 −(aq)
However, the aluminum(III) ion actually reacts with six water molecules to form a stable complex ion, and so the more explicit representation of the dissolution process is
Al(NO3)3(s) + 6H2O(l) ⇌ Al(H2O)6 3+(aq) + 3NO3 −(aq)
As shown in Figure 14.13, the Al(H2O)6 3+ ions involve bonds between a central Al atom and the O atoms of the six water molecules. Consequently, the bonded water molecules' O–H bonds are more polar than in nonbonded water molecules, making the bonded molecules more prone to donation of a hydrogen ion:
Al(H2O)6 3+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Al(H2O)5(OH)2+(aq) Ka = 1.4 × 10−5
The conjugate base produced by this process contains five other bonded water molecules capable of acting as acids, and so the sequential or step-wise transfer of protons is possible as depicted in few equations below:
Al(H2O)6 3+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Al(H2O)5(OH)2+(aq)
Al(H2O)5(OH)2+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Al(H2O)4(OH)2 +(aq)
Al(H2O)4(OH)2 +(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Al(H2O)3(OH)3(aq)
This is an example of a polyprotic acid, the topic of discussion in a later section of this chapter.
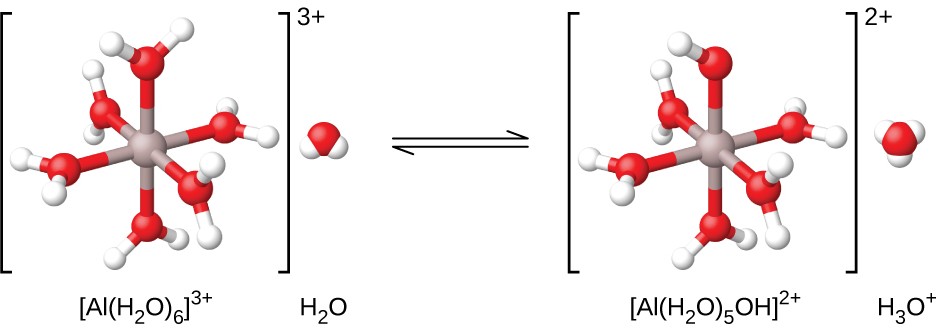
Figure 14.13 When an aluminum ion reacts with water, the hydrated aluminum ion becomes a weak acid.
Aside from the alkali metals (group 1) and some alkaline earth metals (group 2), most other metal ions will undergo acid ionization to some extent when dissolved in water. The acid strength of these complex ions typically increases with increasing charge and decreasing size of the metal ions. The first-step acid ionization equations for a few other acidic metal ions are shown below:
Fe(H2O)6 3+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+(aq) pKa = 2.74
Cu(H2O)6 2+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Cu(H2O)5(OH)+(aq) pKa = ~ 6.3
Zn(H2O)4 2+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Zn(H2O)3(OH)+(aq) pKa = 9.6
Example 14.18
Hydrolysis of [Al(H2O)6]3+
Calculate the pH of a 0.10-M solution of aluminum chloride, which dissolves completely to give the hydrated aluminum ion [Al(H2O)6]3+ in solution.
Solution
The equation for the reaction and Ka are:
Al(H2O)6 3+(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + Al(H2O)5(OH)2+(aq) Ka = 1.4 × 10−5
An ICE table with the provided information is
| Al(H2O)6 3+(aq) + H2O(l) | ⇌H3O+ | + Al(H2O)5(OH)2+ | |
| Initial Concentration (M) | 0.10 | ~0 | 0 |
| Change (M) | -x | +x | +x |
| Equilibrium Concentration (M) | 0.10 - x | x | x |
Substituting the expressions for the equilibrium concentrations into the equation for the ionization constant yields:
Ka = [latex]\frac{[H_{3}O^{+}][Al(H_{2}O)_{5}(OH)^{2+}]}{[Al(H_{2}O)_{6}^{3+}]}[/latex]
= [latex]\frac{(x)(x)}{0.10 - x}[/latex] = 1.4 x 10-5
Assuming x << 0.10 and solving the simplified equation gives:
x = 1.2 × 10−3 M
The ICE table defined x as equal to the hydronium ion concentration, and so the pH is calculated to be
[H3O+] = 0 + x = 1.2 × 10−3 M
pH = −log[H3O+] = 2.92 (an acidic solution)
Check Your Learning
What is [Al(H2O)5(OH)2+] in a 0.15-M solution of Al(NO3)3 that contains enough of the strong acid HNO3 to bring [H3O+] to 0.10 M?
Answer: 2.1 × 10−5 M