20 Quality Management
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should be able to:
- Understand the elements of a quality management program.
- Define quality planning, quality assurance and quality control.
- Determine core components of the various quality management program items.
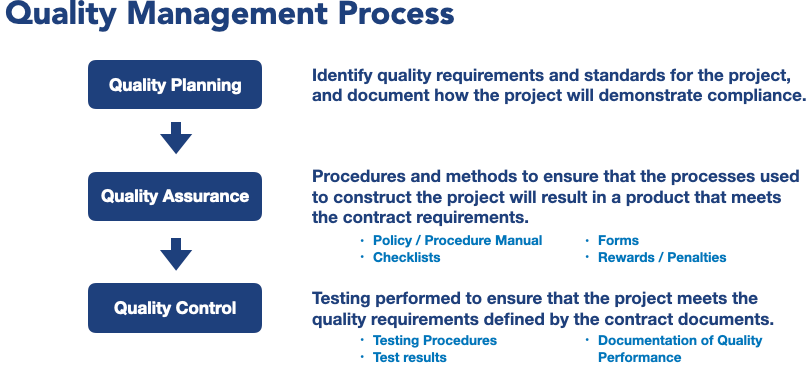
Quality management is focused on planning for quality, developing processes and procedures to ensure quality design and construction, and performing testing to validate that a product meets the defined quality standard. These are defined within the Project Management Body of Knowledge as the three aspects of Quality Management (also see Figure 1):
- Quality Planning
- Quality Assurance
- Quality Control
Who is Responsible for Quality on a Project?
Just like everyone on a project is responsible for safety, it is also true that everyone should be participating in the management of quality. The quality management process starts very early in the lifecycle of a project.
The Owner’s Responsibilities:
The owner plays a critical role in the quality management process. One of the most critical items in the delivery process is to ensure that the owner, possibly working with other service providers, develops a detailed program that outlines the overall quality goals and any specific requirements that they may have for the project. This program should set a clear picture of the expected levels of scope and quality for the project. A program can include qualitative information regarding the desired levels of quality on a project, along with specific quantitative and prescriptive descriptions, e.g., the size of various spaces or a specific material or system desired within a building. In addition to the program, many larger owners have their own set of design guidelines that outline specific requirements, e.g., preferences on material such as using rigid conduit instead of flex conduit in specific locations even if the building code would allow flex conduit. This combination of program and design guidelines informs the design process. If they are not well done, the owner may not obtain their level of desired quality (and scope).
Once a project enters the design process, the owner must continue to provide timely and decisive feedback related to the project design. Owners need to make many decisions, and for large owners, the process of managing all stakeholders can be an extensive task. For example, if a university is designing a classroom, office, and lab building, the owner will need to coordinate feedback from many user groups, including the academic units, lab managers, academic administrators, and the physical plant team that will maintain the building. Therefore, it can be challenging to get timely feedback for some decisions. Having an owner’s representative who can provide timely feedback is critical to the success of projects.
Review Questions

