Kemp Model of Design
Introduction
The Kemp model, sometimes referred to as the Morrison, Ross and Kemp Model, has the four elements of design that are an integral part course development: students, objectives, methods, and evaluation. The emphasis of this model is the interdependencies of each of the steps in the process with the belief that instructional design is a continuous cycle with “revision” being an ongoing process to improve and adjust as needed. It is also unique in its non-linear structure and the interrelated nature of those main components allowing for flexibility as the ID moves through the nine stages of this design. These stages can be addressed simultaneously, individually, or in some cases- not at all. The Kemp model encourages the designers to take the perspective of the learner so that their needs, priorities, and constraints are taken into consideration as the objectives, course material, and assessments are created and implemented.
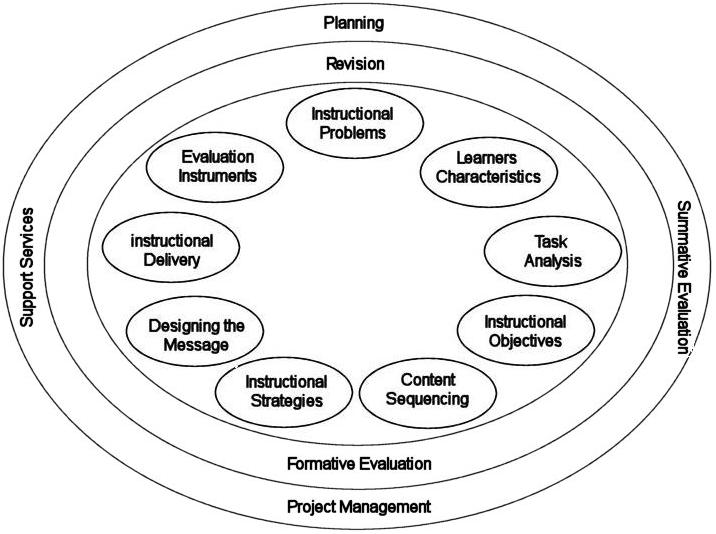
The Nine Design Elements of the Kemp Model
- Determine the specific goals and instructional issues.
- Identify the characteristics and needs of the learners that should be taken into account.
- Clarify the course content and analyze the proposed task components in relationship to the set goals.
- Define the instructional objectives and learning outcomes.
- Ensure the content for each component of instruction is sequentially and logically presented.
- Design instructional strategies to enable learners to master the content and achieve the learning outcomes.
- Plan the instructional message and the appropriate mode of delivery.
- Develop the evaluation instruments suitable for measuring and assessing learners’ progress toward achieving the course obejctives
- Choose appropriate resources that will support the teaching and learning activities.
The following presentation outlines the key components of the Kemp Model and the Dick & Carey Model of Design.
Handouts
References
Giles, M. (2013). The Kemp ID Model. [Internet]. Available from http://www.slideshare.net/lindamgiles/kemp-id-modelpresmgiles-16411696 Accessed 3rd January 2018
Gustafson, K. L., & Branch, R. M. (2002). What is instructional design? In R.A. Reiser & J. A. Dempsey (Eds.), Trends and issues in instructional design and technology (pp. 16-25). Saddle River, NJ: Merrill/Prentice-Hall.
Kemp, J. E. (1985). The instructional design process. New York: Harper & Row.
Kemp, J. E., Morrison, G. R., & Ross, S. V. (1994). Design effective instruction, New York: Macmillan.
Morrison, G. R., Ross, S. M. & Kemp, J. E. (2004). Design effective instruction (4th Ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons
Morrison, G. R., Ross, S. M., Kemp, J. E., & Kalman, H. (2010). Designing effective instruction (6th Ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons.
