Chapter 6.2 – How Changes in Income and Prices Affect Consumption Choices
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how income, prices, and preferences affect consumer choices
- Contrast the substitution effect and the income effect
- Utilize concepts of demand to analyze consumer choices
- Apply utility-maximizing choices to governments and businesses
Just as we can use utility and marginal utility to discuss making consumer choices along a budget constraint, we can also use these ideas to think about how consumer choices change when the budget constraint shifts in response to changes in income or price. Because we can use the budget constraint framework to analyze how quantities demanded
change because of price movements, the budget constraint model can illustrate the underlying logic behind demand curves.
How Changes in Income Affect Consumer Choices
Let’s begin with a concrete example illustrating how changes in income level affect consumer choices. Figure 6.2 shows a budget constraint that represents Kimberly’s choice between concert tickets at $50 each and getting away overnight to a bed-and-breakfast for $200 per night. Kimberly has $1,000 per year to spend between these two
choices. After thinking about her total utility and marginal utility and applying the decision rule that the ratio of the marginal utilities to the prices should be equal between the two products, Kimberly chooses point M, with eight concerts and three overnight getaways as her utility-maximizing choice.
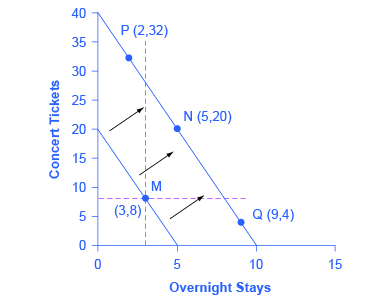
If overnight stays is an inferior good, Kimberly will make a choice like P. If concert tickets are an inferior good, Kimberly will make a choice like Q. How a Change in Income Affects Consumption Choices. By Openstax. Source: Openstax. CC BY 4.0
Now, assume that the income Kimberly has to spend on these two items rises to $2,000 per year, causing her budget constraint to shift out to the right. How does this rise in income alter her utility-maximizing choice? Kimberly will again consider the utility and marginal utility that she receives from concert tickets and overnight getaways and seek her utility-maximizing choice on the new budget line, but how will her new choice relate to her original choice?
We can replace the possible choices along the new budget constraint into three groups, which the dashed horizontal and vertical lines that pass through the original choice M in the figure divide. All choices on the upper left of the new budget constraint that are to the left of the vertical dashed line, like choice P with two overnight stays and 32 concert tickets, involve less of the good on the horizontal axis but much more of the good on the vertical axis. All choices to the right of the vertical dashed line and above the horizontal dashed line—like choice N with five overnight getaways and 20 concert tickets—have more consumption of both goods. Finally, all choices that are to the right of the vertical dashed line but below the horizontal dashed line, like choice Q with four concerts and nine overnight getaways, involve less of the good on the vertical axis but much more of the good on the horizontal axis.
All of these choices are theoretically possible, depending on Kimberly’s personal preferences as expressed through the total and marginal utility she would receive from consuming these two goods. When income rises, the most common reaction is to purchase more of both goods, like choice N, which is to the upper right relative to Kimberly’s original choice M, although exactly how much more of each good will vary according to personal taste. Conversely, when income falls, the most typical reaction is to purchase less of both goods. As we defined in the chapter on Demand and Supply and again in the chapter on Elasticity, we call goods and services normal goods when a rise in income leads to a rise in the quantity consumed of that good and a fall in income leads to a fall in quantity consumed.
However, depending on Kimberly’s preferences, a rise in income could cause consumption of one good to increase while consumption of the other good declines. A choice like P means that a rise in income caused her quantity consumed of overnight stays to decline, while a choice like Q would mean that a rise in income caused her quantity of concerts to decline. Goods where demand declines as income rises (or conversely, where the demand rises as income falls) are called “inferior goods.” An inferior good occurs when people trim back on a good as income rises, because they can now afford the more expensive choices that they prefer. For example, a higher-income household might eat fewer hamburgers or be less likely to buy a used car, and instead eat more steak and buy a new car.
How Price Changes Affect
Consumer Choices
For analyzing the possible effect of a change in price on consumption, let’s again use a concrete example. Figure 6.3 represents Sergei's consumer choice, who chooses between purchasing baseball bats and cameras. A price increase for baseball bats would have no effect on the ability to purchase cameras, but it would reduce the number of bats Sergei could afford to buy. Thus a price increase for baseball bats, the good on the horizontal axis, causes the budget constraint to rotate inward, as if on a hinge, from the vertical axis. As in the previous section, the point labeled M represents the originally preferred point on the original budget constraint, which Sergei has chosen after contemplating his total utility and marginal utility and the tradeoffs involved along the budget constraint. In this example, the units along the horizontal and vertical axes are not numbered, so the discussion must focus on whether Sergei will consume more or less of certain goods, not on numerical amounts.
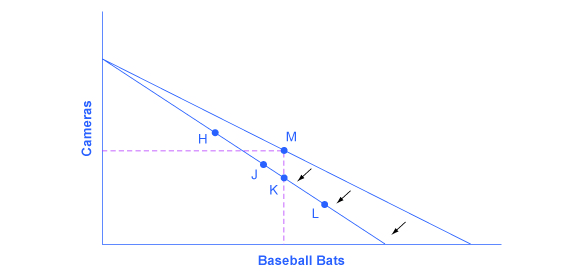
After the price increase, Sergei will make a choice along the new budget constraint. Again, we can divide his choices into three segments by the dashed vertical and horizontal lines. In the upper-left portion of the new budget constraint, at a choice like H, Sergei consumes more cameras and fewer bats. In the central portion of the new budget constraint, at a choice like J, he consumes less of both goods. At the right-hand end, at a choice like L, he consumes more bats but fewer cameras. The typical response to higher prices is that a person chooses to consume less of the product with the higher price. This occurs for two reasons, and both effects can occur simultaneously. The substitution effect occurs when a price changes and consumers have an incentive to consume less of the good with a relatively higher price and more of the good with a relatively lower price. The income effect is that a higher price means, in effect, the buying power of income has been reduced (even though actual income has not changed), which leads to buying less of the good (when the good is normal). In this example, the higher price for baseball bats would cause Sergei to buy fewer bats for both reasons. Exactly how much will a higher price for bats cause Sergei's bat consumption to fall? Figure 6.3 suggests a range of possibilities. Sergei might react to a higher price for baseball bats by purchasing the same quantity of bats, but cutting his camera consumption. This choice is the point K on the new budget constraint, straight below the original choice M. Alternatively, Sergei might react by dramatically reducing his bat purchases and instead buy more cameras.
The key is that it would be imprudent to assume that a change in baseball bats will only or primarily affect the good's price whose price is changed, while the quantity consumed of other goods remains the same. Since Sergei purchases all his products out of the same budget, a change in the price of one good can also have a range of effects, either positive or negative, on the quantity consumed of other goods.
In short, a higher price typically causes reduced consumption of the good in question, but it can affect the consumption of other goods as well.
The Foundations of Demand Curves
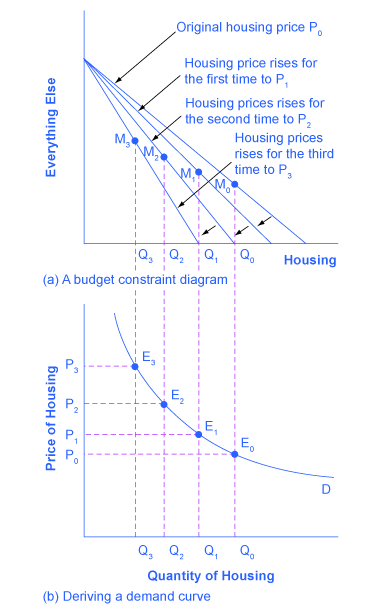
Changes in the price of a good lead the budget constraint to rotate. A rotation in the budget constraint means that when individuals are seeking their highest utility, the quantity that is demanded of that good will change. In this way, the logical foundations of demand curves—which show a connection between prices and quantity demanded—are based on the underlying idea of individuals seeking utility. Figure 6.4 (a) shows a budget constraint with a choice between housing and “everything else.” (Putting “everything else” on the vertical axis can be a useful approach in some cases, especially when the focus of the analysis is on one particular good.) We label the preferred choice on the original budget constraint that provides the highest possible utility [latex]M_0[/latex]. The other three budget constraints represent successively higher prices for housing of [latex]P_1[/latex], [latex]P_2[/latex], and [latex]P_3[/latex]. As the budget constraint rotates in, and in, and in again, we label the utility-maximizing choices [latex]M_1[/latex], [latex]M_2[/latex], and [latex]M_3[/latex], and the quantity demanded of housing falls from [latex]Q_0[/latex] to [latex]Q_1[/latex] to [latex]Q_2[/latex] to [latex]Q3[/latex].
Applications in Government and Business
The budget constraint framework for making utility-maximizing choices offers a reminder that people can react to a change in price or income in a range of different ways. For example, in the winter months of 2005, costs for heating homes increased significantly in many parts of the country as prices for natural gas and electricity soared, due in large part to the disruption caused by Hurricanes Katrina and Rita. Some people reacted by reducing the quantity demanded of energy; for example, by turning down the thermostats in their homes by a few degrees and wearing a heavier sweater inside. Even so, many home heating bills rose, so people adjusted their consumption in other ways, too. As you learned in the chapter on Elasticity, the short-run demand for home heating is generally inelastic. Each household cut back on what it valued least on the margin. For some, it might have been some dinners out, or a vacation, or postponing buying a new refrigerator or a new car. Sharply higher energy prices can have effects beyond the energy market, leading to a widespread reduction in purchasing throughout the rest of the economy.
A similar issue arises when the government imposes taxes on certain products, such as gasoline, cigarettes, and alcohol. Say that a tax on alcohol leads to a higher price at the liquor store. The higher price of alcohol causes the budget constraint to pivot left, and alcoholic beverage consumption is likely to decrease. However, people may also react to the higher price of alcoholic beverages by cutting back on other purchases. For example, they might cut back on snacks at restaurants like chicken wings and nachos. It would be unwise to assume that the liquor industry is the only one affected by the tax on alcoholic beverages. Read the next Clear It Up to learn about how who controls the household income influences buying decisions.
The Unifying Power of the Utility-Maximizing Budget Set Framework
An interaction between prices, budget constraints, and personal preferences determine household choices. The flexible and powerful terminology of utility-maximizing gives economists a vocabulary for bringing these elements together.
Not even economists believe that people walk around mumbling about their marginal utilities before they walk into a shopping mall, accept a job, or make a deposit in a savings account. However, economists do believe that individuals seek their own satisfaction or utility and that people often decide to try a little less of one thing and a little more of another. If we accept these assumptions, then the idea of utility-maximizing households facing budget constraints becomes highly plausible.
CLEAR IT UP
Does who controls household income make a difference?
In the mid-1970s, the United Kingdom made an interesting policy change in its “child allowance” policy. This program provides a fixed amount of money per child to every family, regardless of family income. Traditionally, the child allowance had been distributed to families by withholding less in taxes from the paycheck of the family wage earner—typically the father in this time period. The new policy instead provided the child allowance as a cash payment to the mother. As a result of this change, households have the same level of income and face the same prices in the market, but the money is more likely to be in the mother's purse than in the father's wallet.
Should this change in policy alter household consumption patterns? Basic models of consumption decisions, of the sort that we examined in this chapter, assume that it does not matter whether the mother or the father receives the money because both parents seek to maximize the family's utility as a whole. In effect, this model assumes that everyone in the family has the same preferences.
In reality, the share of that the father or mother controls does affect what the household consumes. When the mother controls a larger share of family income a number of studies, in the United Kingdom and in a wide variety of other countries, have found that the family tends to spend more on restaurant meals, childcare, and women’s clothing, and less on alcohol and tobacco. As the mother controls a larger share of household resources, children’s health improves, too. These findings suggest that when providing assistance to poor families, in high-income countries and low-income countries alike, the monetary amount of assistance is not all that matters: it also matters which family member actually receives the money.

