8.6 – Photosynthesis
Learning Objectives
- Describe the function and locations of photosynthetic pigments in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
- Describe the major products of the light-dependent and light-independent reactions
- Describe the reactions that produce glucose in a photosynthetic cell
- Compare and contrast cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
Heterotrophic organisms ranging from E. coli to humans rely on the chemical energy found mainly in carbohydrate molecules. Many of these carbohydrates are produced by photosynthesis, the biochemical process by which phototrophic organisms convert solar energy (sunlight) into chemical energy. Although photosynthesis is most commonly associated with plants, microbial photosynthesis is also a significant supplier of chemical energy, fueling many diverse ecosystems. In this section, we will focus on microbial photosynthesis.
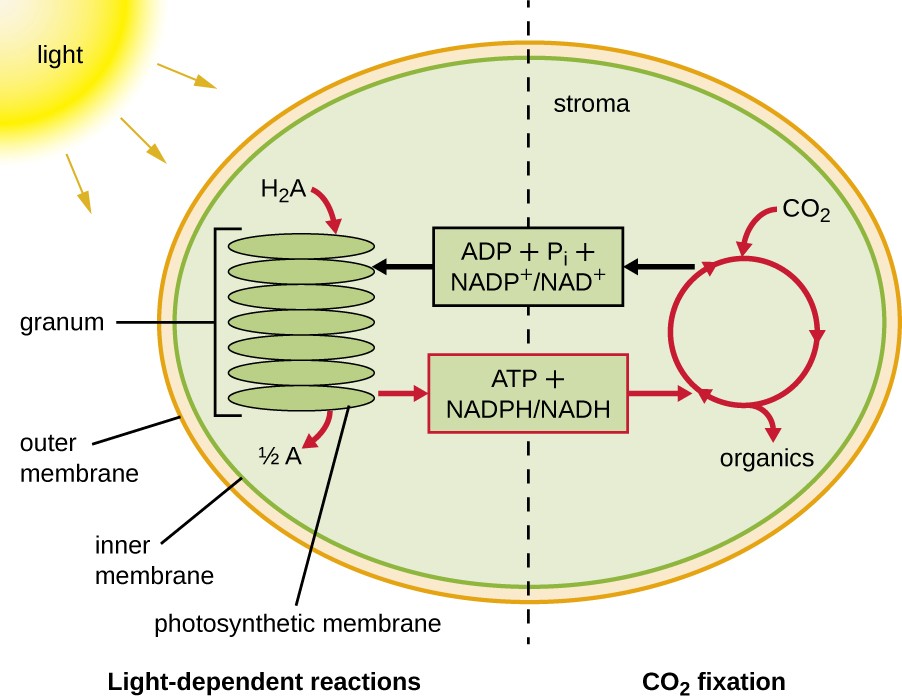
Photosynthesis takes place in two sequential stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent reactions (Figure 8.19). In the light-dependent reactions, energy from sunlight is absorbed by pigment molecules in photosynthetic membranes and converted into stored chemical energy. In the light-independent reactions, the chemical energy produced by the light-dependent reactions is used to drive the assembly of sugar molecules using CO2; however, these reactions are still light dependent because the products of the light-dependent reactions necessary for driving them are short-lived. The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and either NADPH or NADH to temporarily store energy. These energy carriers are used in the light-independent reactions to drive the energetically unfavorable process of “fixing” inorganic CO2 in an organic form, sugar.
Photosynthetic Structures in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
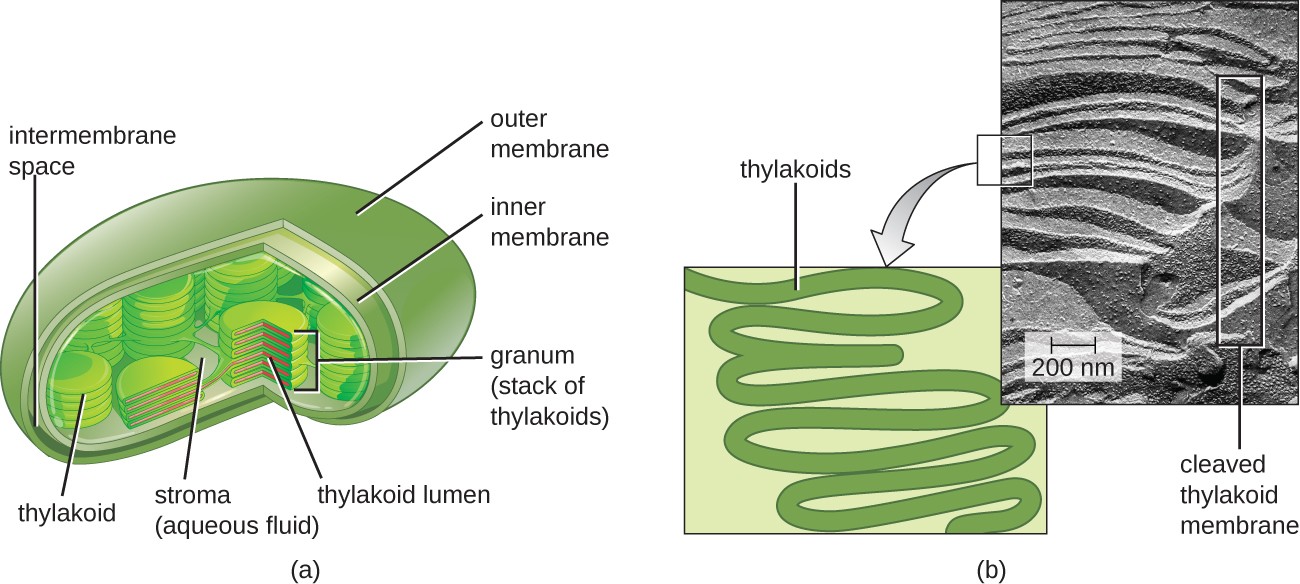
In all phototrophic eukaryotes, photosynthesis takes place inside a chloroplast, an organelle that arose in eukaryotes by endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic bacterium (see Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells). These chloroplasts are enclosed by a double membrane with inner and outer layers. Within the chloroplast is a third membrane that forms stacked, disc-shaped photosynthetic structures called thylakoids (Figure 8.20). A stack of thylakoids is called a granum, and the space surrounding the granum within the chloroplast is called stroma.
Photosynthetic membranes in prokaryotes, by contrast, are not organized into distinct membrane-enclosed organelles; rather, they are infolded regions of the plasma membrane. In cyanobacteria, for example, these infolded regions are also referred to as thylakoids. In either case, embedded within the thylakoid membranes or other photosynthetic bacterial membranes are photosynthetic pigment molecules organized into one or more photosystems, where light energy is actually converted into chemical energy.
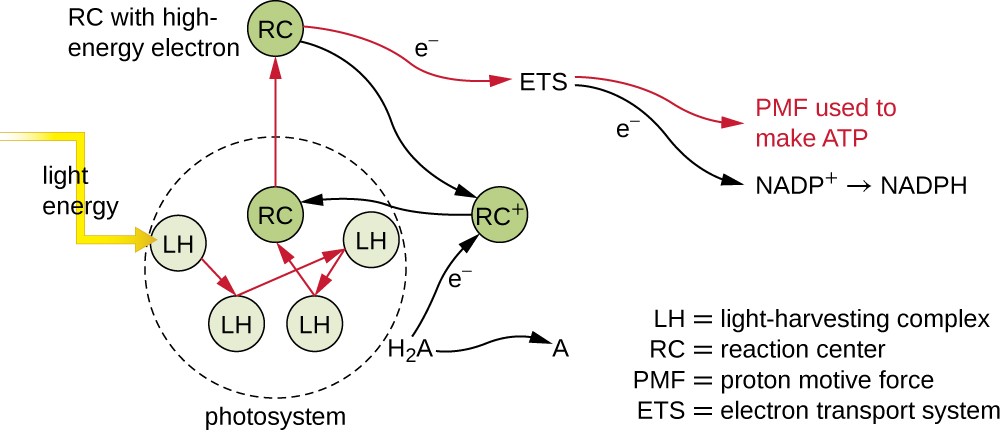
Photosynthetic pigments within the photosynthetic membranes are organized into photosystems, each of which is composed of a light-harvesting (antennae) complex and a reaction center. The light-harvesting complex consists of multiple proteins and associated pigments that each may absorb light energy and, thus, become excited. This energy is transferred from one pigment molecule to another until eventually (after about a millionth of a second) it is delivered to the reaction center. Up to this point, only energy—not electrons—has been transferred between molecules. The reaction center contains a pigment molecule that can undergo oxidation upon excitation, actually giving up an electron. It is at this step in photosynthesis that light energy is converted into an excited electron.
Different kinds of light-harvesting pigments absorb unique patterns of wavelengths (colors) of visible light. Pigments reflect or transmit the wavelengths they cannot absorb, making them appear the corresponding color. Examples of photosynthetic pigments (molecules used to absorb solar energy) are bacteriochlorophylls (green, purple, or red), carotenoids (orange, red, or yellow), chlorophylls (green), phycocyanins (blue), and phycoerythrins (red). By having mixtures of pigments, an organism can absorb energy from more wavelengths. Because photosynthetic bacteria commonly grow in competition for sunlight, each type of photosynthetic bacteria is optimized for harvesting the wavelengths of light to which it is commonly exposed, leading to stratification of microbial communities in aquatic and soil ecosystems by light quality and penetration.
Once the light harvesting complex transfers the energy to the reaction center, the reaction center delivers its high-energy electrons, one by one, to an electron carrier in an electron transport system, and electron transfer through the ETS is initiated. The ETS is similar to that used in cellular respiration and is embedded within the photosynthetic membrane. Ultimately, the electron is used to produce NADH or NADPH. The electrochemical gradient that forms across the photosynthetic membrane is used to generate ATP by chemiosmosis through the process of photophosphorylation, another example of oxidative phosphorylation (Figure 8.21).
Check Your Understanding
- In a phototrophic eukaryote, where does photosynthesis take place?
Oxygenic and Anoxygenic Photosynthesis
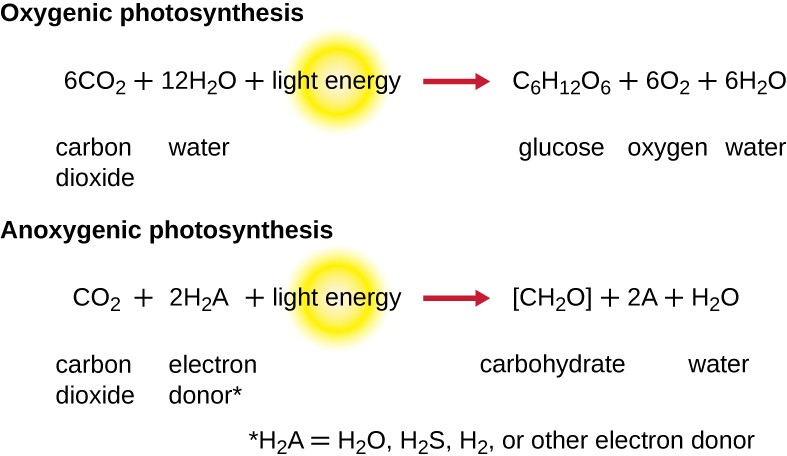
For photosynthesis to continue, the electron lost from the reaction center pigment must be replaced. The source of this electron (H2A) differentiates the oxygenic photosynthesis of plants and cyanobacteria from anoxygenic photosynthesis carried out by other types of bacterial phototrophs (Figure 8.22). In oxygenic photosynthesis, H2O is split and supplies the electron to the reaction center. Because oxygen is generated as a byproduct and is released, this type of photosynthesis is referred to as oxygenic photosynthesis. However, when other reduced compounds serve as the electron donor, oxygen is not generated; these types of photosynthesis are called anoxygenic photosynthesis.
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) or thiosulfate ($$S_2O_3^{2-}$$) S subscript 2 O subscript 3 superscript 2 minus end superscript can serve as the electron donor, generating elemental sulfur and sulfate ($$SO_4^{2-}$$) ions, respectively, as a result.
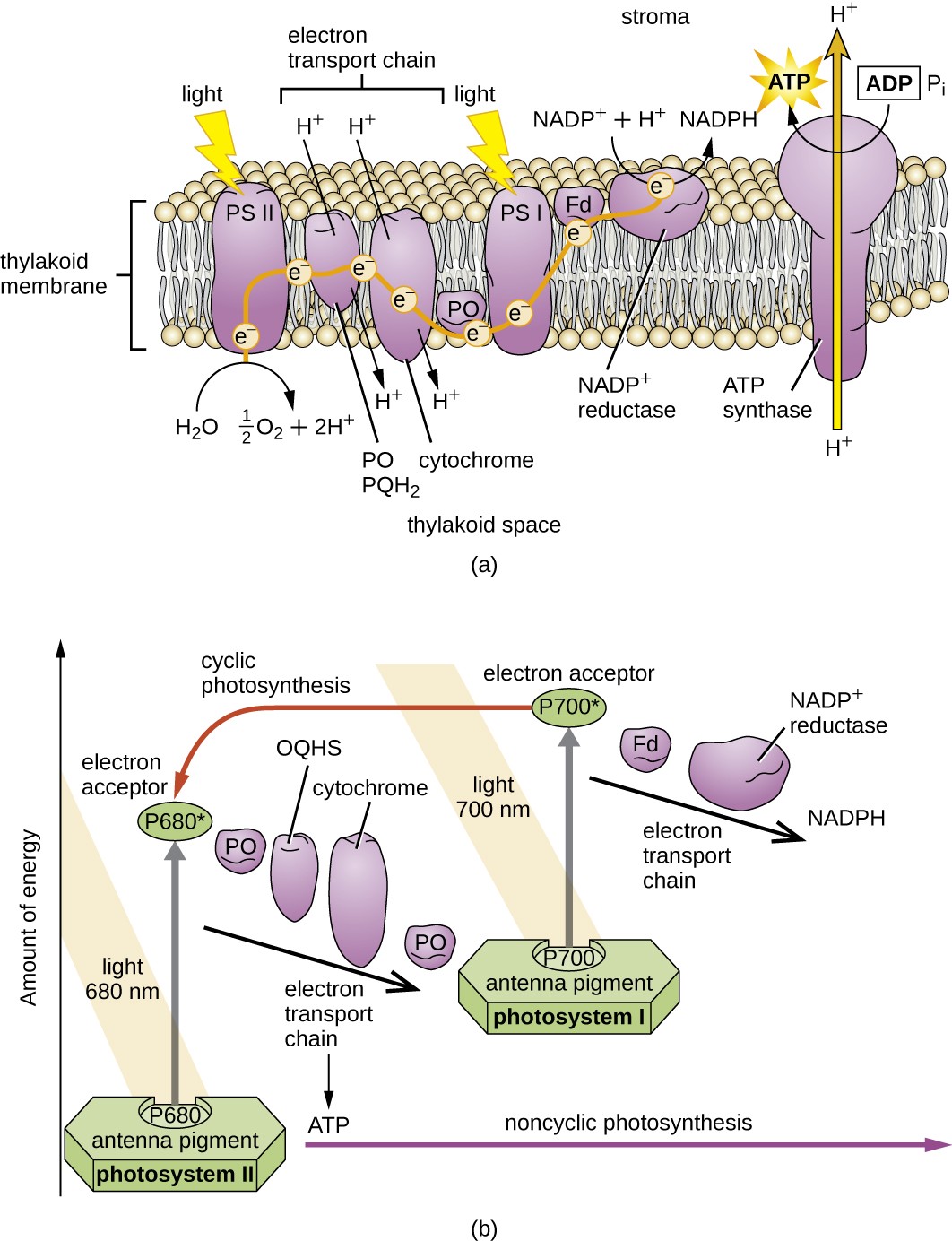
Photosystems have been classified into two types: photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII) (Figure 8.23). Cyanobacteria and plant chloroplasts have both photosystems, whereas anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria use only one of the photosystems. Both photosystems are excited by light energy simultaneously. If the cell requires both ATP and NADPH for biosynthesis, then it will carry out noncyclic photophosphorylation. Upon passing of the PSII reaction center electron to the ETS that connects PSII and PSI, the lost electron from the PSII reaction center is replaced by the splitting of water. The excited PSI reaction center electron is used to reduce NADP+ to NADPH and is replaced by the electron exiting the ETS. The flow of electrons in this way is called the Z-scheme.
If a cell’s need for ATP is significantly greater than its need for NADPH, it may bypass the production of reducing power through cyclic photophosphorylation. Only PSI is used during cyclic photophosphorylation; the high-energy electron of the PSI reaction center is passed to an ETS carrier and then ultimately returns to the oxidized PSI reaction center pigment, thereby reducing it.
Check Your Understanding
- Why would a photosynthetic bacterium have different pigments?
Light-Independent Reactions
After the energy from the sun is converted into chemical energy and temporarily stored in ATP and NADPH molecules (having lifespans of millionths of a second), photoautotrophs have the fuel needed to build multicarbon carbohydrate molecules, which can survive for hundreds of millions of years, for long-term energy storage. The carbon comes from CO2, the gas that is a waste product of cellular respiration.
The Calvin-Benson cycle (named for Melvin Calvin [1911–1997] and Andrew Benson [1917–2015]), the biochemical pathway used for fixation of CO2, is located within the cytoplasm of photosynthetic bacteria and in the stroma of eukaryotic chloroplasts. The light-independent reactions of the Calvin cycle can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration (see Appendix C for a detailed illustration of the Calvin cycle).
- Fixation: The enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) catalyzes the addition of a CO2 to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). This results in the production of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- Reduction: Six molecules of both ATP and NADPH (from the light-dependent reactions) are used to convert 3-PGA into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). Some G3P is then used to build glucose.
- Regeneration: The remaining G3P not used to synthesize glucose is used to regenerate RuBP, enabling the system to continue CO2 fixation. Three more molecules of ATP are used in these regeneration reactions.
The Calvin cycle is used extensively by plants and photoautotrophic bacteria, and the enzyme RuBisCO is said to be the most plentiful enzyme on earth, composing 30%–50% of the total soluble protein in plant chloroplasts.[1]
However, besides its prevalent use in photoautotrophs, the Calvin cycle is also used by many nonphotosynthetic chemoautotrophs to fix CO2. Additionally, other bacteria and archaea use alternative systems for CO2 fixation. Although most bacteria using Calvin cycle alternatives are chemoautotrophic, certain green sulfur photoautotrophic bacteria have been also shown to use an alternative CO2 fixation pathway.
Check Your Understanding
- Describe the three stages of the Calvin cycle.
Footnote
1. Dhingra et al. “Enhanced Translation of a Chloroplast-Expressed RbcS Gene Restores Small Subunit Levels and Photosynthesis in Nuclear RbcS Antisense Plants.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 101 no. 16 (2004):6315–6320.

