11.3 – RNA Transcription
Learning Objectives
- Explain how RNA is synthesized using DNA as a template
- Distinguish between transcription in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
During the process of transcription, the information encoded within the DNA sequence of one or more genes is transcribed into a strand of RNA, also called an RNA transcript. The resulting single-stranded RNA molecule, composed of ribonucleotides containing the bases adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and uracil (U), acts as a mobile molecular copy of the original DNA sequence. Transcription in prokaryotes and in eukaryotes requires the DNA double helix to partially unwind in the region of RNA synthesis. The unwound region is called a transcription bubble. Transcription of a particular gene always proceeds from one of the two DNA strands that acts as a template, the so-called antisense strand. The RNA product is complementary to the template strand of DNA and is almost identical to the nontemplate DNA strand, or the sense strand. The only difference is that in RNA, all of the T nucleotides are replaced with U nucleotides; during RNA synthesis, U is incorporated when there is an A in the complementary antisense strand.
Transcription in Bacteria
Bacteria use the same RNA polymerase to transcribe all of their genes. Like DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase adds nucleotides one by one to the 3’-OH group of the growing nucleotide chain. One critical difference in activity between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase is the requirement for a 3’-OH onto which to add nucleotides: DNA polymerase requires such a 3’-OH group, thus necessitating a primer, whereas RNA polymerase does not. During transcription, a ribonucleotide complementary to the DNA template strand is added to the growing RNA strand and a covalent phosphodiester bond is formed by dehydration synthesis between the new nucleotide and the last one added. In E. coli, RNA polymerase comprises six polypeptide subunits, five of which compose the polymerase core enzyme responsible for adding RNA nucleotides to a growing strand. The sixth subunit is known as sigma (σ). The σ factor enables RNA polymerase to bind to a specific promoter, thus allowing for the transcription of various genes. There are various σ factors that allow for transcription of various genes.
Initiation
The initiation of transcription begins at a promoter, a DNA sequence onto which the transcription machinery binds and initiates transcription. The nucleotide pair in the DNA double helix that corresponds to the site from which the first 5’ RNA nucleotide is transcribed is the initiation site. Nucleotides preceding the initiation site are designated “upstream,” whereas nucleotides following the initiation site are called “downstream” nucleotides. In most cases, promoters are located just upstream of the genes they regulate. Although promoter sequences vary among bacterial genomes, a few elements are conserved. At the –10 and –35 positions within the DNA prior to the initiation site (designated +1), there are two promoter consensus sequences, or regions that are similar across all promoters and across various bacterial species. The –10 consensus sequence, called the TATA box, is TATAAT. The –35 sequence is recognized and bound by σ.
Elongation
The elongation in transcription phase begins when the σ subunit dissociates from the polymerase, allowing the core enzyme to synthesize RNA complementary to the DNA template in a 5’ to 3’ direction at a rate of approximately 40 nucleotides per second. As elongation proceeds, the DNA is continuously unwound ahead of the core enzyme and rewound behind it (Figure 11.11).
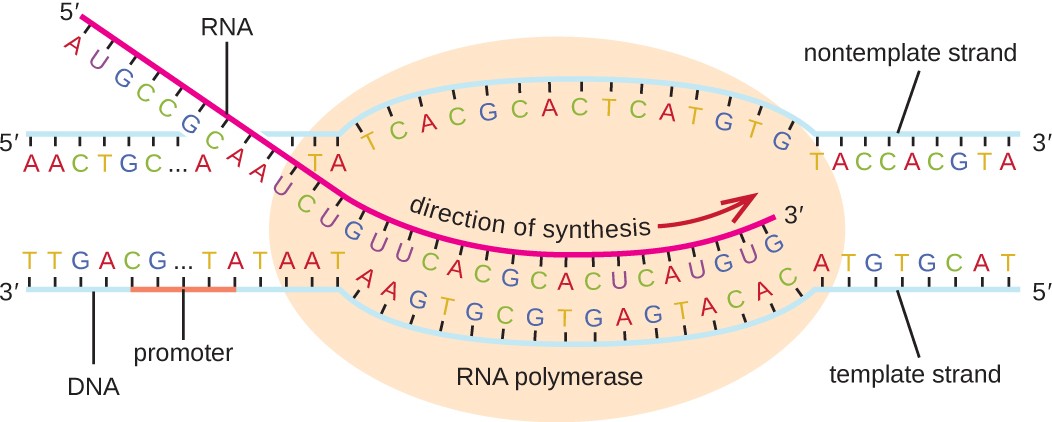
Diagram of transcription. A double stranded piece of DNA has a large oval labeled RNA polymerase sitting on it just past a region labeled promoter. The DNA in the RNA polymerase has separated and the bottom DNA strand (labeled template strand) has a newly forming RNA strand attached to it. The RNA strand is being built from 5’ to 3’. The other strand of DNA is the nontemplate strand and does not have RNA being built.
Termination
Once a gene is transcribed, the bacterial polymerase must dissociate from the DNA template and liberate the newly made RNA. This is referred to as termination of transcription. The DNA template includes repeated nucleotide sequences that act as termination signals, causing RNA polymerase to stall and release from the DNA template, freeing the RNA transcript.
Check Your Understanding
- Where does σ factor of RNA polymerase bind DNA to start transcription?
- What occurs to initiate the polymerization activity of RNA polymerase?
- Where does the signal to end transcription come from?
Transcription in Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process of transcription, with a few significant differences (see Table 11.3). Eukaryotes use three different polymerases, RNA polymerases I, II, and III, all structurally distinct from the bacterial RNA polymerase. Each transcribes a different subset of genes. Interestingly, archaea contain a single RNA polymerase that is more closely related to eukaryotic RNA polymerase II than to its bacterial counterpart. Eukaryotic mRNAs are also usually monocistronic, meaning that they each encode only a single polypeptide, whereas prokaryotic mRNAs of bacteria and archaea are commonly polycistronic, meaning that they encode multiple polypeptides.
The most important difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is the latter’s membrane-bound nucleus, which influences the ease of use of RNA molecules for protein synthesis. With the genes bound in a nucleus, the eukaryotic cell must transport protein-encoding RNA molecules to the cytoplasm to be translated. Protein-encoding primary transcripts, the RNA molecules directly synthesized by RNA polymerase, must undergo several processing steps to protect these RNA molecules from degradation during the time they are transferred from the nucleus to the cytoplasm and translated into a protein. For example, eukaryotic mRNAs may last for several hours, whereas the typical prokaryotic mRNA lasts no more than 5 seconds.
The primary transcript (also called pre-mRNA) is first coated with RNA-stabilizing proteins to protect it from degradation while it is processed and exported out of the nucleus. The first type of processing begins while the primary transcript is still being synthesized; a special 7-methylguanosine nucleotide, called the 5’ cap, is added to the 5’ end of the growing transcript. In addition to preventing degradation, factors involved in subsequent protein synthesis recognize the cap, which helps initiate translation by ribosomes. Once elongation is complete, another processing enzyme then adds a string of approximately 200 adenine nucleotides to the 3’ end, called the poly-A tail. This modification further protects the pre-mRNA from degradation and signals to cellular factors that the transcript needs to be exported to the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotic genes that encode polypeptides are composed of coding sequences called exons (ex-on signifies that they are expressed) and intervening sequences called introns (int-ron denotes their intervening role). Transcribed RNA sequences corresponding to introns do not encode regions of the functional polypeptide and are removed from the pre- mRNA during processing. It is essential that all of the intron-encoded RNA sequences are completely and precisely removed from a pre-mRNA before protein synthesis so that the exon-encoded RNA sequences are properly joined together to code for a functional polypeptide. If the process errs by even a single nucleotide, the sequences of the rejoined exons would be shifted, and the resulting polypeptide would be nonfunctional. The process of removing intron-encoded RNA sequences and reconnecting those encoded by exons is called RNA splicing and is facilitated by the action of a spliceosome containing small nuclear ribonucleo proteins (snRNPs). Intron-encoded RNA sequences are removed from the pre-mRNA while it is still in the nucleus. Although they are not translated, introns appear to have various functions, including gene regulation and mRNA transport. On completion of these modifications, the mature transcript, the mRNA that encodes a polypeptide, is transported out of the nucleus, destined for the cytoplasm for translation. Introns can be spliced out differently, resulting in various exons being included or excluded from the final mRNA product. This process is known as alternative splicing. The advantage of alternative splicing is that different types of mRNA transcripts can be generated, all derived from the same DNA sequence. In recent years, it has been shown that some archaea also have the ability to splice their pre-mRNA.
Comparison of Transcription in Bacteria Versus Eukaryotes
| Property | Bacteria | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Number of polypeptides encoded per mRNA | Monocistronic or polycistronic | Exclusively monocistronic |
| Strand elongation | core + σ = holoenzyme | RNA polymerases I, II, or III |
| Addition of 5’ cap | No | Yes |
| Addition of 3’ poly-A tail | No | Yes |
| Splicing of pre-mRNA | No | Yes |
Link to Learning
Visualize how mRNA splicing happens by watching the process in action in this video.
See how introns are removed during RNA splicing in this second video.
Check Your Understanding
- In eukaryotic cells, how is the RNA transcript from a gene for a protein modified after it is transcribed?
- Do exons or introns contain information for protein sequences?

