Chapter 1: Stress
Good Stress?
Although stress carries a negative connotation, at times it may be of some benefit. Stress can motivate us to do things in our best interests, such as study for exams, visit the doctor regularly, exercise, and perform to the best of our ability at work. Indeed, Selye (1974) pointed out that not all stress is harmful. He argued that stress can sometimes be a positive, motivating force that can improve the quality of our lives. This kind of stress, which Selye called eustress (from the Greek eu = “good”), is a good kind of stress associated with positive feelings, optimal health, and performance. A moderate amount of stress can be beneficial in challenging situations. For example, athletes may be motivated and energized by pregame stress, and students may experience similar beneficial stress before a major exam. Indeed, research shows that moderate stress can enhance both immediate and delayed recall of educational material. Male participants in one study who memorized a scientific text passage showed improved memory of the passage immediately after exposure to a mild stressor as well as one day following exposure to the stressor (Hupbach & Fieman, 2012).
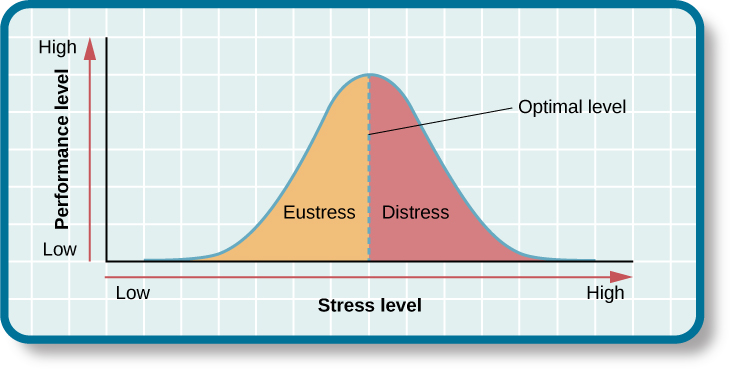
Increasing one’s level of stress will cause performance to change in a predictable way. As shown in Figure 3.0, as stress increases, so do performance and general well-being (eustress); when stress levels reach an optimal level (the highest point of the curve), performance reaches its peak. A person at this stress level is colloquially at the top of his game, meaning he feels fully energized, focused, and can work with minimal effort and maximum efficiency. But when stress exceeds this optimal level, it is no longer a positive force—it becomes excessive and debilitating, or what Selye termed distress (from the Latin dis = “bad”). People who reach this level of stress feel burned out; they are fatigued, exhausted, and their performance begins to decline. If the stress remains excessive, health may begin to erode as well (Everly & Lating, 2002).
Test your knowledge

