Executive Summary
A Building Information Model (BIM) is “a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility.” To successfully implement BIM, a project team must perform detailed and comprehensive planning. A well-documented BIM Project Execution Plan (BEP) will ensure that all parties are clearly aware of the opportunities and responsibilities associated with the incorporation of BIM into the project workflow. A completed BEP should define the appropriate Model Uses for a project (e.g., author design model, design review, and 3D coordination), along with a detailed design and documentation of the process for executing BIM throughout a facility’s lifecycle. Once the plan is created, the team can follow and monitor their progress against this plan to gain the maximum benefits from BIM implementation.
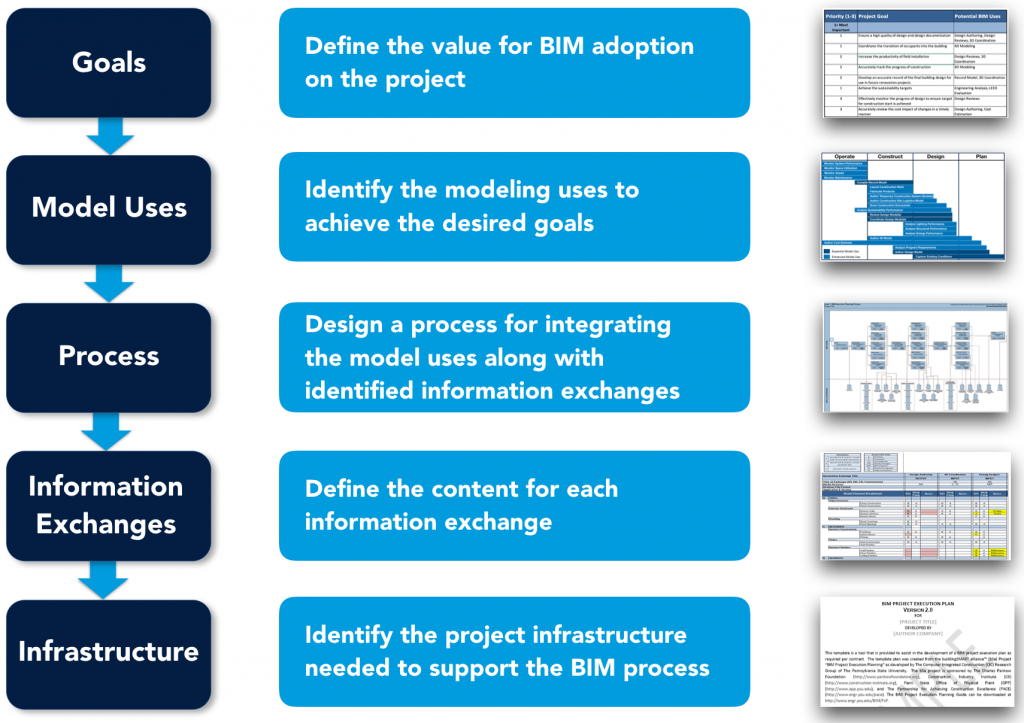
This Guide provides a structured procedure, as displayed in Figure i-1, for creating and implementing a BEP. The five steps within the procedure include:
- Define the goals for the implementation of BIM;
- Identify high-value Model Uses during project planning, design, construction, and operational phases;
- Design the BIM execution process by creating process maps;
- Define the information deliverables; and
- Develop the infrastructure in the form of contracts, communication procedures, technology, and quality control to support the implementation.
The objective for following the structured procedure is to stimulate planning and direct communication among the project team members during the early phases of a project. The team leading the planning process should include members from all organizations with a significant role in the project. Since there is no single best method for BIM implementation on every project, each team must effectively design a tailored execution strategy by understanding the project goals, the project characteristics, and the capabilities of the team members.
This BIM Project Execution Planning Guide is a product of the BIM Project Execution Planning Project within the buildingSMART alliance™ (bSa), a council within the National Institute of Building Sciences. The bSa is charged with developing the National Building Information Modeling Standard – United States™ (NBIMS-US). This Guide was developed to provide a practical manual that can be used by project teams to design their BIM strategy and develop a BEP. The core modeling and information exchange concepts have been designed to complement the long-term goals of the bSa in the development of a standard that can be implemented throughout the AECOO Industry to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of BIM implementation on projects.
a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life-cycle; defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition. A basic premise of BIM is collaboration by different stakeholders at different phases of the life cycle of a facility to insert, extract, update or modify information in the BIM to support and reflect the roles of that stakeholder.
Source: National BIM Standard - US, Version 1.0
The BIM Execution Plan (BEP) is a plan developed by the project team that defines how BIM will be implemented throughout the project lifecycle.
A method of applying Building Information Modeling during a facility’s lifecycle to achieve one or more specific objectives.
Note: The term 'Model Use' was referred to as 'BIM Use' in previous versions of this Guide.

