11.5 – Sodium
Learning Objectives
- Discuss the roles of sodium in the body
- List food groups that are dietary sources of sodium and ways to reduce daily sodium intake.
Sodium is vital not only for maintaining fluid balance but also for many other essential body functions. In contrast to many minerals, sodium absorption in the small intestine is extremely efficient and in a healthy individual, all excess sodium is excreted by the kidneys. In fact, very little sodium is required in the diet (about 200 milligrams) because the kidneys actively reabsorb sodium. Kidney reabsorption of sodium is hormonally controlled, allowing for a relatively constant sodium concentration in the blood.
The typical American diet today is quite high in sodium, often providing > 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day. This is especially true if a person eats a lot of processed or packaged foods. For young people with healthy kidneys, excess sodium intake may not be a problem. However, high sodium intake can have serious consequences for people with compromised kidney function. In addition, during the normal aging process, the kidneys often become less efficient at excreting excess sodium from the blood. In either case, the result of compromised kidney function is the retention of fluid in the blood leading to higher pressure within the blood vessels. This condition is known as high blood pressure or hypertension, and can often be controlled by reducing the amount of sodium consumed.
Other Functions of Sodium in the Body
The second notable function of sodium is in nerve impulse transmission. Nerve impulse transmission results from the transport of sodium cations into a nerve cell, which creates a charge difference (or voltage) between the nerve cell and its extracellular environment. Similar to how a current moves along a wire, a sodium current moves along a nerve cell. Stimulating a muscle contraction also involves the movement of sodium ions as well as other ion movements.
Sodium is essential for nutrient absorption in the small intestine and also for nutrient reabsorption in the kidney. Amino acids, glucose, and water must make their way from the small intestine to the blood. To do so, they pass through intestinal cells on their way to the blood. The transport of nutrients through intestinal cells is facilitated by the sodium-potassium pump, which by moving sodium out of the cell, creates a higher sodium concentration outside of the cell (requiring A.T.P.).
Sodium Imbalances
Sweating is a homeostatic mechanism for maintaining body temperature, which influences fluid and electrolyte balance. Sweat is mostly water but also contains some electrolytes, mostly sodium and chloride. Under normal environmental conditions (i.e., not hot, humid days) water and sodium loss through sweat is negligible but is highly variable among individuals. It is estimated that sixty minutes of high-intensity physical activity, like playing a game of tennis, can produce approximately one liter of sweat; however, the amount of sweat produced is highly dependent on environmental conditions. A liter of sweat typically contains between 1 and 2 grams of sodium and therefore exercising for multiple hours can result in a high amount of sodium loss in some people. Additionally, hard labor can produce substantial sodium loss through sweat. In either case, the lost sodium is easily replaced in the next snack or meal.
In athletes, hyponatremia, or a low blood sodium level, is not so much the result of excessive sodium loss in sweat, but rather drinking too much water. The excess water dilutes the sodium concentration in blood. Illnesses causing vomiting, sweating, and diarrhea may also cause hyponatremia. The symptoms of hyponatremia, also called water intoxication (since it is often the root cause) include nausea, muscle cramps, confusion, dizziness, and in severe cases, coma and death. The physiological events that occur in water intoxication are the following:
- Excessive sodium loss and/or water intake.
- Sodium levels fall in blood and in the fluid between cells.
- Water moves to where solutes are more concentrated (i.e. into cells).
- Cells swell.
- Symptoms, including nausea, muscle cramps, confusion, dizziness, and in severe cases, coma and death result.
Hyponatremia in endurance athletes (such as marathon runners) can be avoided by drinking the correct amount of water, which is about 1-2 cups of water per hour during the event.1 Attention should be paid to urine color, thirst, and typical weight loss during activity can help an athlete customize fluid needs. Sports drinks are better at restoring fluid and blood-glucose levels than replacing electrolytes. During an endurance event, it is important to practice to find a refueling plan that meets the athlete’s goals for fuel, fluid, and gut comfort. This may include utilizing fuel sources ranging from liquids to solids.
If you’re not exercising over an hour at high intensity, you can skip the sports drinks, but not the water. For those who do not exercise or do so at low to moderate intensity, sports drinks are simply another source of extra calories, sugar, and salt.2
1 Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2016;116 (3) 501-528. Accessed June 30, 2019.
2 Convertino VA, et al. American College of Sports Medicine Position Stand. Exercise and Fluid Replacement. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1996; 28(1) i–vii. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9303999. Accessed June 30, 2019.
Needs and Dietary Sources of Sodium
The I.O.M. has set an A.I. level for sodium for healthy adults between the ages of nineteen and fifty at 1,500 milligrams (Table 11.5.1 ). Table salt is approximately 40 percent sodium and 60 percent chloride. As a reference point, just ⅔ teaspoon of salt is needed in the diet to meet the A.I. for sodium. The A.I. takes into account the amount of sodium lost in sweat during recommended physical activity levels and additionally provides for the sufficient intake of other nutrients, such as chloride. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (U.L.) for sodium is 2,300 milligrams per day for adults. (Just over 1 teaspoon of salt contains the 2,300 milligrams of sodium recommended). The U.L. is considered appropriate for healthy individuals but not those with hypertension (high blood pressure). The I.O.M. estimates that greater than 95 percent of men and 75 percent of women in America consume salt in excess of the U.L.. Many scientific studies demonstrate that reducing salt intake prevents hypertension, is helpful in reducing blood pressure after hypertension is diagnosed, and reduces the risk for cardiovascular disease. The I.O.M. recommends that people over fifty, African Americans, diabetics, and those with chronic kidney disease should consume no more than 1,500 milligrams of sodium per day. The American Heart Association (A.H.A.) states that all Americans, not just those listed, should consume less than 1,500 milligrams of sodium per day to prevent cardiovascular disease. The A.H.A. recommends this because millions of people have risk factors for hypertension and there is scientific evidence supporting that lower-sodium diets are preventive against hypertension.
| Age Group | Adequate Intake (milligrams per day) | C.D.R.R. (Chronic Disease Risk Reduction Intake) |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 110 | Not Determined |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 370 | Not Determined |
| Children (1–3 years) | 800 | 1,200 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 1,000 | 1,500 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 1,200 | 1,800 |
| Adolescents and Adults (14 years and older) | 1,500 | 2,300 |
Source: Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. Institute of Medicine. . Accessed May 29, 2019.
Food Sources for Sodium
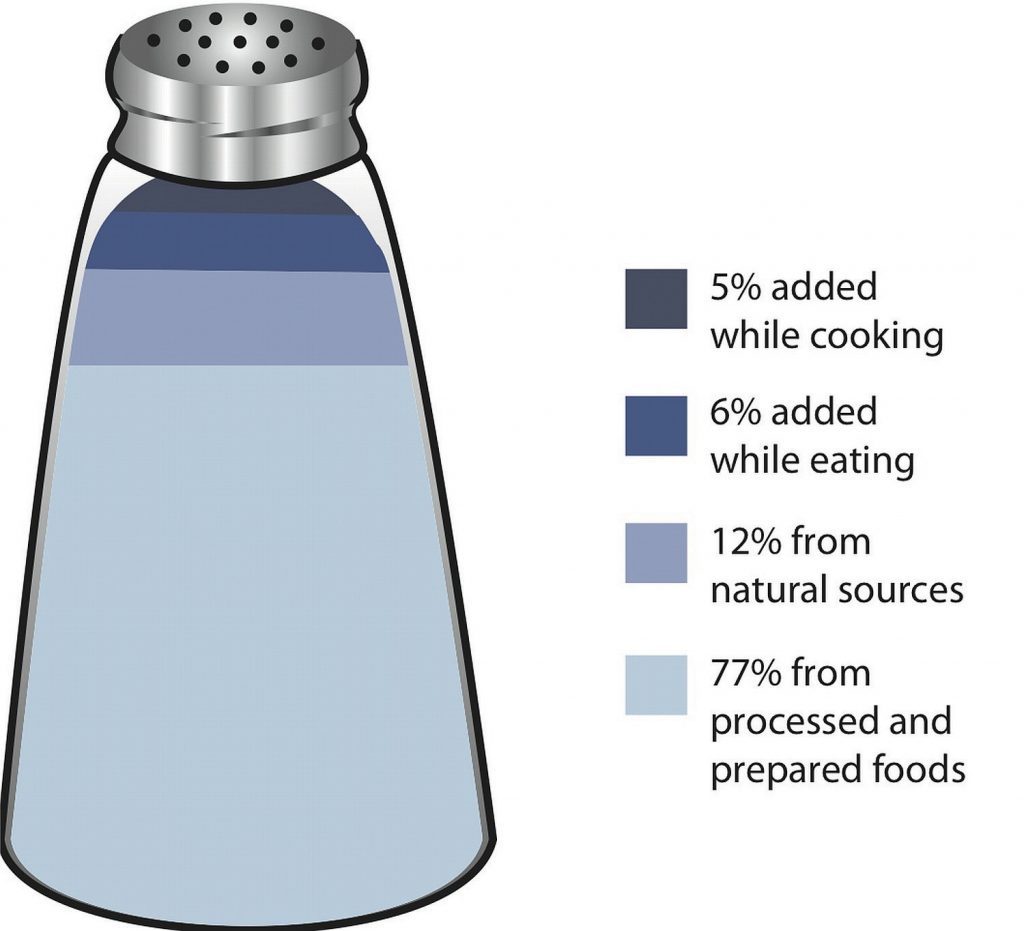
Most sodium in the typical American diet comes from processed and prepared foods. Manufacturers add salt to foods to improve texture and flavor, and also as a preservative. The amount of salt in similar food products varies widely. Some foods, such as meat, poultry, and dairy foods, contain naturally-occurring sodium. For example, one cup of low-fat milk contains 107 milligrams of sodium. Naturally-occurring sodium accounts for less than 12 percent of dietary intake in a typical diet. For the sodium contents of various foods see Table 11.5.2.
| Food | Serving Size | Sodium(milligrams) |
|---|---|---|
| Breads, all types | 1 oz. | 95–210 |
| Rice Chex cereal | 1 ¼ c. | 292 |
| Raisin Bran cereal | 1 c. | 362 |
| Frozen pizza, plain, cheese | 4 oz | 450–1200 |
| Frozen vegetables, all types | ½ c. | 2–160 |
| Salad dressing, regular fat, all types | 2 Tbsp. | 110–505 |
| Salsa | 2 Tbsp. | 150–240 |
| Soup (tomato), reconstituted | 8 oz. | 700–1260 |
| Potato chips | 1 oz. (28.4 g) | 120–180 |
| Tortilla chips | 1 oz. (28.4 g) | 105–160 |
| Pork | 3 oz. | 59 |
| Chicken | (½ breast) | 69 |
| Chicken fast food dinner | Not Determined | 2243 |
| Chicken noodle soup | 1 c. | 1107 |
| Dill pickle | 1 | 928 |
| Soy sauce | 1 Tbsp. | 1029 |
| Canned corn | 1 c. | 384 |
| Baked beans, canned | 1 c. | 856 |
| Hot dog | 1 | 639 |
| Burger, fast-food | 1 | 990 |
| Steak | 3 oz. | 55 |
| Canned tuna | 3 oz. | 384 |
| Fresh tuna | 3 oz. | 50 |
| Dry-roasted peanuts | 1 c. | 986 |
| American cheese | 1 oz. | 406 |
| Tap water | 8 oz. | 12 |
Sodium on the Nutrition Facts Panel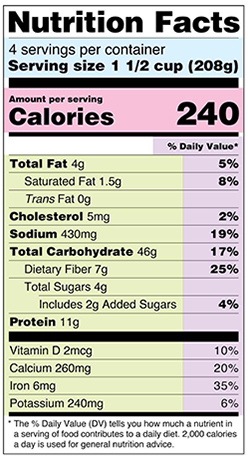
Figure 11.5.2: Nutrition Label. Sodium levels in milligrams is a required listing on a Nutrition Facts label.
The Nutrition Facts panel displays the amount of sodium (in milligrams) per serving of the food in question (Figure 11.5.2). Food additives are often high in sodium, for example, monosodium glutamate (MSG) contains 12 percent sodium. Additionally, baking soda, baking powder, disodium phosphate, sodium alginate, and sodium nitrate or nitrite contain a significant proportion of sodium as well. When you see a food’s Nutrition Facts label, you can check the ingredient list to identify the source of the added sodium. Various claims about the sodium content in foods must be in accordance with the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations (Table 11.5.3 “Food Packaging Claims Regarding Sodium”).
Table 11.5.3: Food Packaging Claims Regarding Sodium.
| Claim | Meaning |
|---|---|
| “Light in Sodium” or “Low in Sodium” | Sodium is reduced by at least 50 percent |
| “No Salt Added” or “Unsalted” | No salt added during preparation and processing* |
| “Lightly Salted” | 50 percent less sodium than that added to similar food |
| “Sodium Free” or “Salt-Free” | Contains less than 5 mg sodium per serving |
| “Very Low Salt” | Contains less than 35 mg sodium per serving |
| “Low Salt” | Contains less than 140 mg sodium per serving |
*Must also declare on the package “This is not a sodium-free food” if food is not sodium-free
Source: Food Labeling Guide. US Food and Drug Administration.Updated June 18, 2019.Accessed June 30, 2019.
Tools for Change
To decrease your sodium intake, become a salt-savvy shopper by reading the label and the ingredient list of processed foods and choosing those lower in salt. Even better, stay away from processed foods and control the seasoning of your foods. Eating a diet with less salty foods diminishes salt cravings so you may need to try a lower sodium diet for a week or two before you will be satisfied with the less salty food. If you have been diagnosed with hypertension, consider following the D.A.S.H. diet described in more detail in Chapter 3.
Salt Substitutes
For those with hypertension or those looking for a way to decrease salt use, using a salt substitute for food preparation is one option. However, many salt substitutes still contain sodium, just in lesser amounts than table salt. Also, remember that most salt in the diet is not from table-salt use, but from processed foods. Salt substitutes often replace the sodium with potassium. People with kidney disorders often have problems getting rid of excess potassium in the diet and are advised to avoid salt substitutes containing potassium. People with liver disorders should also avoid salt substitutes containing potassium because their treatment is often accompanied by potassium dysregulation.
| Alternative | Implementation of Alternative |
|---|---|
| Allspice | Lean ground meats, stews, tomatoes, peaches, applesauce, cranberry sauce, gravies, lean meat |
| Almond extract | Puddings, fruits |
| Caraway seeds | Lean meats, stews, soups, salads, bread, cabbage, asparagus, noodles |
| Chives | Salads, sauces, soups, lean-meat dishes, vegetables |
| Cider vinegar | Salads, vegetables, sauces |
| Cinnamon | Fruits, bread, pie crusts |
| Curry powder | Lean meats (especially lamb), veal, chicken, fish, tomatoes, tomato soup, mayonnaise, |
| Dill | fish sauces, soups, tomatoes, cabbages, carrots, cauliflower, green beans, cucumbers, potatoes, salads, macaroni, lamb |
| Garlic (not garlic salt) | Lean meats, fish, soups, salads, vegetables, tomatoes, potatoes |
| Ginger | Chicken, fruits |
| Lemon juice | Lean meats, fish, poultry, salads, vegetables |
| Mace | Hot bread, apples, fruit salads, carrots, cauliflower, squash, potatoes, veal, lamb |
| Mustard (dry) | lean ground meats, lean meats, chicken, fish, salads, asparagus, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, mayonnaise, sauces |
| Nutmeg | Fruits, pie crust, lemonade, potatoes, chicken, fish, lean meatloaf, toast, veal, pudding |
| Onion powder | Lean meats, stews, vegetables, salads, soups |
| Paprika | Lean meats, fish, soups, salads, sauces, vegetables |
| Parsley | Lean meats, fish, soups, salads, sauces, vegetables |
| Peppermint extract | Puddings, fruits |
| Pimiento | Salads, vegetables, casserole dishes |
| Rosemary | Chicken, veal, lean meatloaf, lean beef, lean pork, sauces, stuffings, potatoes, peas, lima beans |
| Sage | Lean meats, stews, biscuits, tomatoes, green beans, fish, lima beans, onions, lean pork |
| Savory | Salads, lean pork, lean ground meats, soups, green beans, squash, tomatoes, lima beans, peas |
| Thyme | Lean meats (especially veal and lean pork), sauces, soups, onions, peas, tomatoes, salads |
| Turmeric | Lean meats, fish, sauces, rice |
Source: Shaking the Salt Habit. American Heart Association.Updated Oct 31, 2016. Accessed June 30, 2019.
Key Takeaways
- Sodium is vital for maintaining fluid balance, nerve impulse transmission, nutrient absorption in the small intestine and also for nutrient reabsorption in the kidney.
- The transport of nutrients through intestinal cells is facilitated by the sodium-potassium pump.
- Most sodium in the typical American diet comes from processed and prepared foods. Read labels and choose foods lower in sodium more often.
Contributors
University of Hawai’i at Mānoa Food Science and Human Nutrition Program: Allison Calabrese, Cheryl Gibby, Billy Meinke, Marie Kainoa Fialkowski Revilla, and Alan Titchenal

