7.3 – The Role of Proteins in Foods: Cooking and Denaturation
Learning Objectives
- Explain the process of denaturation and its consequences. Give an example.
In addition to having many vital functions within the body, proteins perform different roles in our foods by adding certain functional qualities to them. Protein provides food with structure and texture and enables water retention. For example, proteins foam when agitated. (Picture whisking egg whites to make angel food cake. The foam bubbles are what give the angel food cake its airy texture.) Yogurt is another good example of proteins providing texture. Milk proteins called caseins coagulate, increasing yogurt’s thickness. Cooked proteins add some color to foods as the amino group binds with carbohydrates and produces a brown pigment. Eggs are between 10 and 15 percent protein by weight. Most cake recipes use eggs because the egg proteins help bind all the other ingredients together into a uniform cake batter. The proteins aggregate into a network during mixing and baking that gives cake structure.

By Scheinwerfermann – Own work, Public Domain,
Protein Denaturation: Unraveling the Fold
When a cake is baked, the proteins are denatured. Denaturation refers to the physical changes that take place in a protein exposed to abnormal conditions in the environment. Heat, acid, high salt concentrations, alcohol, and mechanical agitation can cause proteins to denature. When a protein denatures, its complicated folded structure unravels, and it becomes just a long strand of amino acids again. Weak chemical forces that hold tertiary and secondary protein structures together are broken when a protein is exposed to unnatural conditions. Because proteins’ function is dependent on their shape, denatured proteins are no longer functional. During cooking the applied heat causes proteins to vibrate. This destroys the weak bonds holding proteins in their complex shape (though this does not happen to the stronger peptide bonds). The unraveled protein strands then stick together, forming an aggregate (or network).
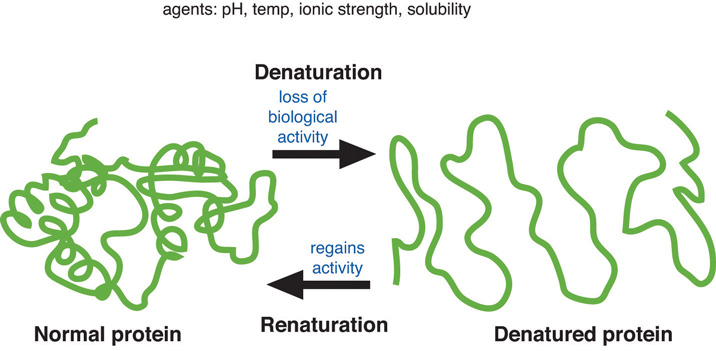
INTERACTIVE 7.3.1: DENATURING OF EGG PROTEINS
Key Takeaways
- Proteins provide food not only with nutrition but also with structure and texture.
- When a protein denatures, its complicated structure unfolds into a strand of amino acids.
Discussion Starters
- Gelatin is a mixture of collagen proteins. How does gelatin add texture and structure to foods? Conduct an experiment by making some Jell-O™ using different methods of denaturation and discuss what happens to the texture and structure.
- Make the first batch of Jell-O™ following the directions. Does it set?
- Next, make up the Jell-O™, but replace hot water with cold. Does it set?
- Instead of adding hot water, add 2 teaspoons of salt and only cold water. Does it set?
- Take the first batch (that is now set) and either whisk it by hand or use an electric mixer. What happens?
- If pouring salt on a live slug produces a puddle of goo, how is it possible to cook snails with salt and get a delicious dish?

