Module 2: Descriptive Statistics
Skewness and the Mean, Median, and Mode
Barbara Illowsky & OpenStax et al.
Consider the following data set.
4; 5; 6; 6; 6; 7; 7; 7; 7; 7; 7; 8; 8; 8; 9; 10
This data set can be represented by following histogram. Each interval has width one, and each value is located in the middle of an interval.
Figure 1.
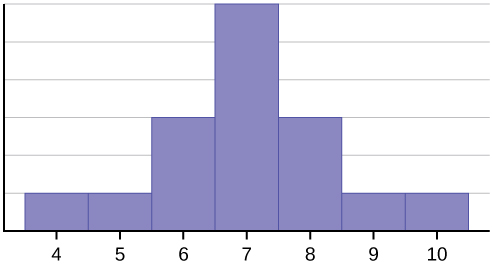
The histogram displays a symmetrical distribution of data. A distribution is symmetrical if a vertical line can be drawn at some point in the histogram such that the shape to the left and the right of the vertical line are mirror images of each other. The mean, the median, and the mode are each seven for these data. In a perfectly symmetrical distribution, the mean and the median are the same. This example has one mode (unimodal), and the mode is the same as the mean and median. In a symmetrical distribution that has two modes (bimodal), the two modes would be different from the mean and median.
The histogram for the data: 4566677778 is not symmetrical. The right-hand side seems “chopped off” compared to the left side. A distribution of this type is called skewed to the left because it is pulled out to the left.
Figure 2.
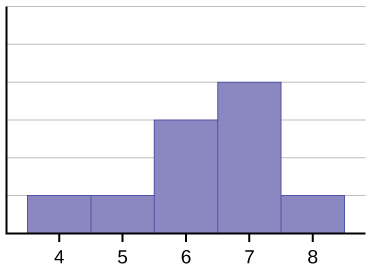
The mean is 6.3, the median is 6.5, and the mode is seven. Notice that the mean is less than the median, and they are both less than the mode. The mean and the median both reflect the skewing, but the mean reflects it more so.
The histogram for the data: 67777888910, is also not symmetrical. It is skewed to the right.
Figure 3.
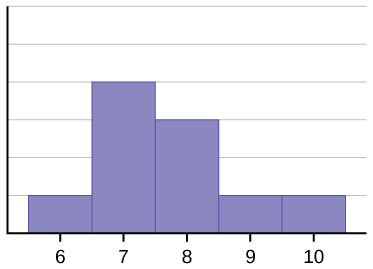
The mean is 7.7, the median is 7.5, and the mode is seven. Of the three statistics, the mean is the largest, while the mode is the smallest. Again, the mean reflects the skewing the most.
To summarize, generally if the distribution of data is skewed to the left, the mean is less than the median, which is often less than the mode. If the distribution of data is skewed to the right, the mode is often less than the median, which is less than the mean.
Skewness and symmetry become important when we discuss probability distributions in later chapters.
Here is a video that summarizes how the mean, median and mode can help us describe the skewness of a dataset. Don’t worry about the terms leptokurtic and platykurtic for this course.
Statistics are used to compare and sometimes identify authors. The following lists shows a simple random sample that compares the letter counts for three authors.
Terry: 7; 9; 3; 3; 3; 4; 1; 3; 2; 2
Davis: 3; 3; 3; 4; 1; 4; 3; 2; 3; 1
Maris: 2; 3; 4; 4; 4; 6; 6; 6; 8; 3
- Make a dot plot for the three authors and compare the shapes.
- Calculate the mean for each.
- Calculate the median for each.
- Describe any pattern you notice between the shape and the measures of center.
try it
Discuss the mean, median, and mode for each of the following problems. Is there a pattern between the shape and measure of the center?
1.

2.
| The Ages Former U.S Presidents Died | |
|---|---|
| 4 | 6 9 |
| 5 | 3 6 7 7 7 8 |
| 6 | 0 0 3 3 4 4 5 6 7 7 7 8 |
| 7 | 0 1 1 2 3 4 7 8 8 9 |
| 8 | 0 1 3 5 8 |
| 9 | 0 0 3 3 |
| Key: 8|0 means 80. | |
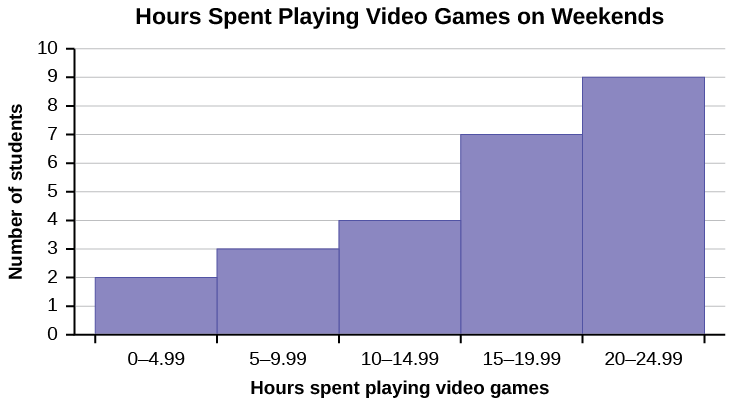
3.
Concept Review
Looking at the distribution of data can reveal a lot about the relationship between the mean, the median, and the mode. There are three types of distributions. A right (or positive) skewed distribution has a shape like Figure 2. A left (or negative) skewed distribution has a shape like Figure 3 . A symmetrical distribution looks like Figure 1.

