Chapter 14 – Emotion Regulation
Response Modulation
Response Modulation occurs after the emotion has already developed. During response modulation, people any of the emotion components. Table 2 outlines the types of emotion regulation.
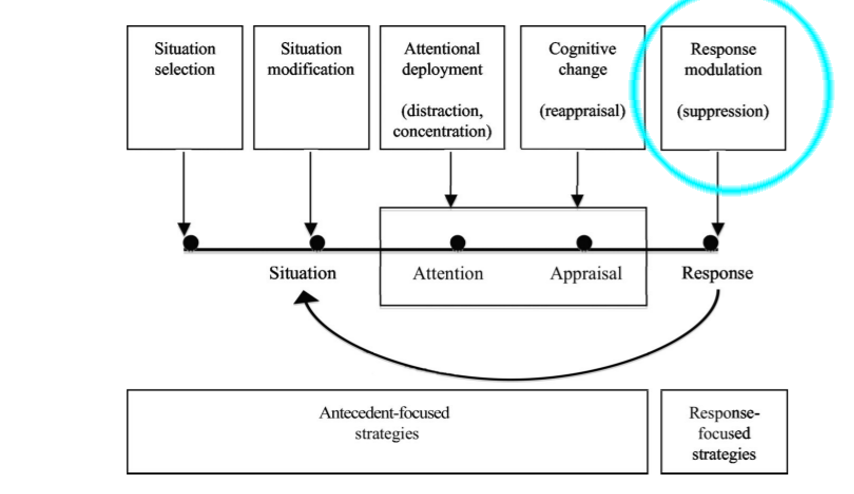
Long Description
The image is a flowchart illustrating emotional regulation strategies. It consists of five boxes arranged horizontally at the top: “Situation selection,” “Situation modification,” “Attentional deployment (distraction, concentration),” “Cognitive change (reappraisal),” and “Response modulation (suppression).” An aqua oval highlights the last box. Arrows point downward from each box to a horizontal timeline labeled “Situation,” “Attention,” “Appraisal,” and “Response.” Arrows on this line indicate the flow from situation to response. Below, there are two labeled rectangles: “Antecedent-focused strategies” spans from “Situation selection” to “Cognitive change,” and “Response-focused strategies” aligns under “Response modulation.”
Table 2
Response Modulation Emotion Regulation Strategies
| Type of Response Modulation | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Changing Subjective Feelings/Physiological Arousal | Changing the valence or activation of our consciously felt emotions |
|
| Changing Behaviors | Changing the behaviors caused by the original emotion. Includes changing facial expressions and vocal changes. |
|
| Changing Thoughts | Suppressing or increasing thoughts to change emotion |
|

